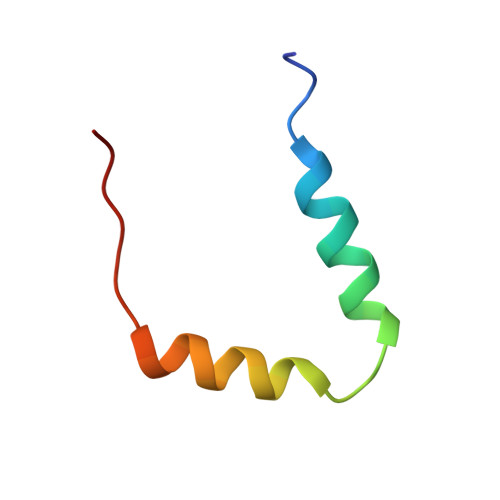
Solution structure of the p53 regulatory domain of the p19Arf tumor suppressor protein.
DiGiammarino, E.L., Filippov, I., Weber, J.D., Bothner, B., Kriwacki, R.W.(2001) Biochemistry 40: 2379-2386
- PubMed: 11327858
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0024005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HN3 - PubMed Abstract:
Arf is a tumor suppressor that regulates p53 function and is a frequent target for loss in human cancers. Through two novel mechanisms, Arf inhibits the oncoprotein Hdm2, a negative regulator of p53. (1) Arf inhibits the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of Hdm2 that leads to p53 degradation, and (2) Arf sequesters Hdm2 within nucleoli. These activities of Arf promote p53-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Fundamental to these processes are interactions between Arf and Hdm2. Here we show that a peptide containing the 37 N-terminal amino acids of mouse Arf (mArfN37) localizes to nucleoli, sequesters Hdm2 within nucleoli, and causes cell cycle arrest. Circular dichroism and NMR spectroscopy show that mArfN37 is largely unstructured under aqueous conditions; however, the peptide adopts two alpha-helices (helix 1, residues 4-14; and helix 2, residues 20-29) in 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (TFE). Each helix contains an amino acid motif that is repeated twice in mArfN37, once in each helix. The two helices, however, do not interact but are connected by an apparently flexible linker. The repeated motif contains Arg residues spaced by a hydrophobic segment that may be involved in Hdm2 recognition and binding. The RRPR nucleolar localization signal, contained within residues 31-34, appears to be disordered under all conditions. The identification of two Arf structural modules suggests that short peptides containing the repeated motif may function as Arf mimics and may allow the design of small molecule Arf mimics in the future.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, Tennessee 38105, USA.