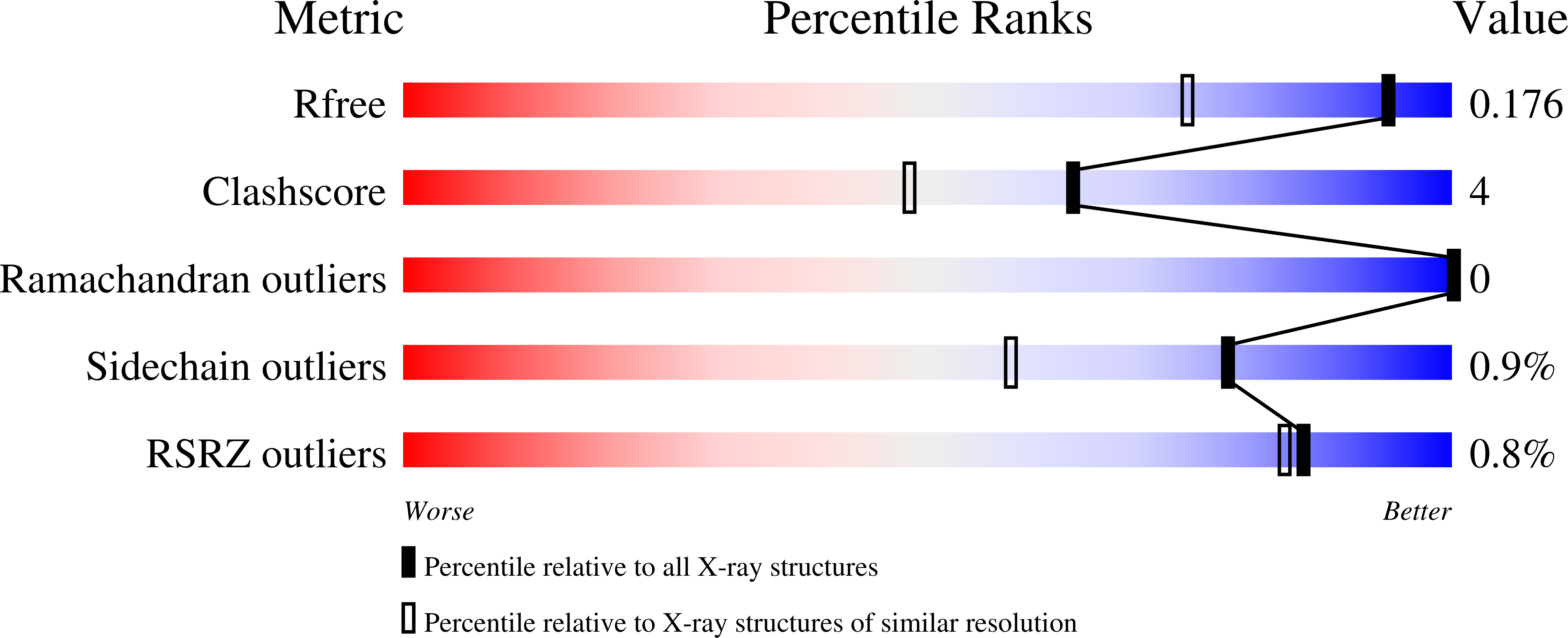
Probing the active site of Class 3 L-asparaginase by mutagenesis. I. Tinkering with the zinc coordination site of ReAV.
Pokrywka, K., Grzechowiak, M., Sliwiak, J., Worsztynowicz, P., Loch, J.I., Ruszkowski, M., Gilski, M., Jaskolski, M.(2024) Front Chem 12: 1381032-1381032
- PubMed: 38638878
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2024.1381032
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8RUA, 8RUD, 8RUE, 8RUF, 8RUG - PubMed Abstract:
ReAV, the inducible Class-3 L-asparaginase from the nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Rhizobium etli , is an interesting candidate for optimizing its enzymatic potential for antileukemic applications. Since it has no structural similarity to known enzymes with this activity, it may offer completely new ways of approach. Also, as an unrelated protein, it would evade the immunological response elicited by other asparaginases. The crystal structure of ReAV revealed a uniquely assembled protein homodimer with a highly specific C135/K138/C189 zinc binding site in each subunit. It was also shown before that the Zn 2+ cation at low and optimal concentration boosts the ReAV activity and improves substrate specificity, which indicates its role in substrate recognition. However, the detailed catalytic mechanism of ReAV is still unknown. In this work, we have applied site-directed mutagenesis coupled with enzymatic assays and X-ray structural analysis to elucidate the role of the residues in the zinc coordination sphere in catalysis. Almost all of the seven ReAV muteins created in this campaign lost the ability to hydrolyze L-asparagine, confirming our predictions about the significance of the selected residues in substrate hydrolysis. We were able to crystallize five of the ReAV mutants and solve their crystal structures, revealing some intriguing changes in the active site area as a result of the mutations. With alanine substitutions of Cys135 or Cys189, the zinc coordination site fell apart and the mutants were unable to bind the Zn 2+ cation. Moreover, the absence of Lys138 induced atomic shifts and conformational changes of the neighboring residues from two active-site Ser-Lys tandems. Ser48 from one of the tandems, which is hypothesized to be the catalytic nucleophile, usually changes its hydration pattern in response to the mutations. Taken together, the results provide many useful clues about the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme, allowing one to cautiously postulate a possible enzymatic scenario.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, Poznan, Poland.