Structural basis for host recognition and superinfection exclusion by bacteriophage T5.
van den Berg, B., Silale, A., Basle, A., Brandner, A.F., Mader, S.L., Khalid, S.(2022) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119: e2211672119-e2211672119
- PubMed: 36215462
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2211672119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8A60, 8A8C - PubMed Abstract:
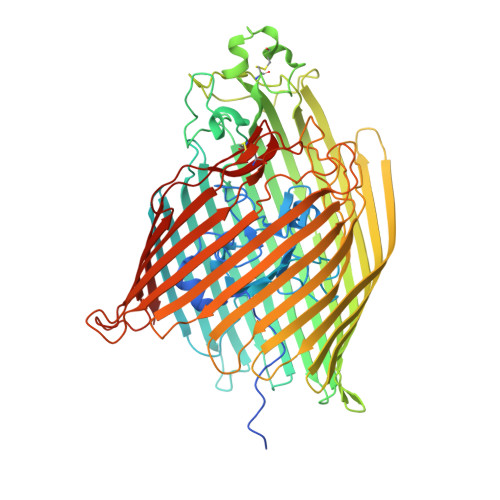
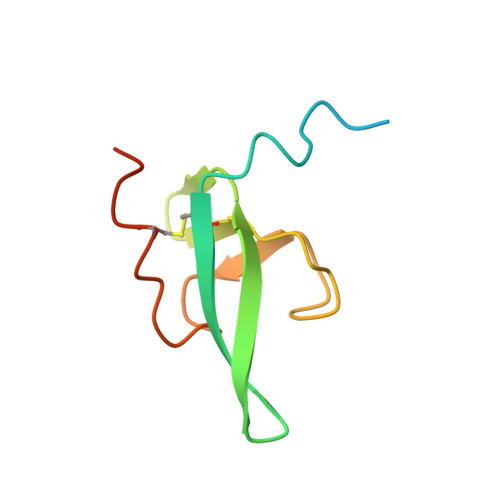
A key but poorly understood stage of the bacteriophage life cycle is the binding of phage receptor-binding proteins (RBPs) to receptors on the host cell surface, leading to injection of the phage genome and, for lytic phages, host cell lysis. To prevent secondary infection by the same or a closely related phage and nonproductive phage adsorption to lysed cell fragments, superinfection exclusion (SE) proteins can prevent the binding of RBPs via modulation of the host receptor structure in ways that are also unclear. Here, we present the cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the phage T5 outer membrane (OM) receptor FhuA in complex with the T5 RBP pb5, and the crystal structure of FhuA complexed to the OM SE lipoprotein Llp. Pb5 inserts four loops deeply into the extracellular lumen of FhuA and contacts the plug but does not cause any conformational changes in the receptor, supporting the view that DNA translocation does not occur through the lumen of OM channels. The FhuA-Llp structure reveals that Llp is periplasmic and binds to a nonnative conformation of the plug of FhuA, causing the inward folding of two extracellular loops via "reverse" allostery. The inward-folded loops of FhuA overlap with the pb5 binding site, explaining how Llp binding to FhuA abolishes further infection of Escherichia coli by phage T5 and suggesting a mechanism for SE via the jamming of TonB-dependent transporters by small phage lipoproteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biosciences Institute, The Medical School, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne NE2 4HH, United Kingdom.