The SiaA/B/C/D signaling network regulates biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Chen, G.K., Gan, J.H., Yang, C., Zuo, Y.L., Peng, J., Li, M., Huo, W.P., Xie, Y.P., Zhang, Y.N., Wang, T.T., Deng, X., Liang, H.H.(2020) EMBO J 39: e103412-e103412
- PubMed: 32090355
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2019103412
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
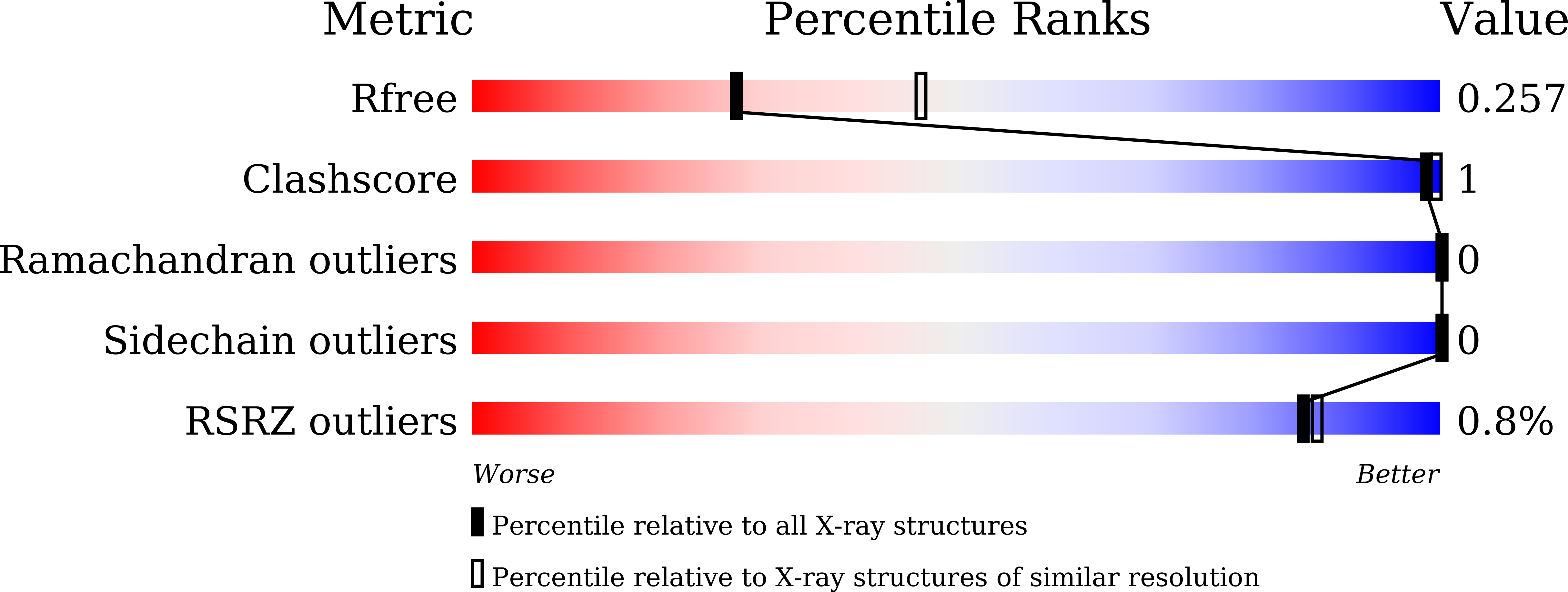
6KKO, 6KKP - PubMed Abstract:
Bacterial cyclic-di-GMP (c-di-GMP) production is associated with biofilm development and the switch from acute to chronic infections. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the diguanylate cyclase (DGC) SiaD and phosphatase SiaA, which are co-transcribed as part of a siaABCD operon, are essential for cellular aggregation. However, the detailed functions of this operon and the relationships among its constituent genes are unknown. Here, we demonstrate that the siaABCD operon encodes for a signaling network that regulates SiaD enzymatic activity to control biofilm and aggregates formation. Through protein-protein interaction, SiaC promotes SiaD diguanylate cyclase activity. Biochemical and structural data revealed that SiaB is an unusual protein kinase that phosphorylates SiaC, whereas SiaA phosphatase can dephosphorylate SiaC. The phosphorylation state of SiaC is critical for its interaction with SiaD, which will switch on or off the DGC activity of SiaD and regulate c-di-GMP levels and subsequent virulence phenotypes. Collectively, our data provide insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying the modulation of DGC activity associated with chronic infections, which may facilitate the development of antimicrobial drugs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Resources Biology and Biotechnology in Western China, Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Northwest University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China.