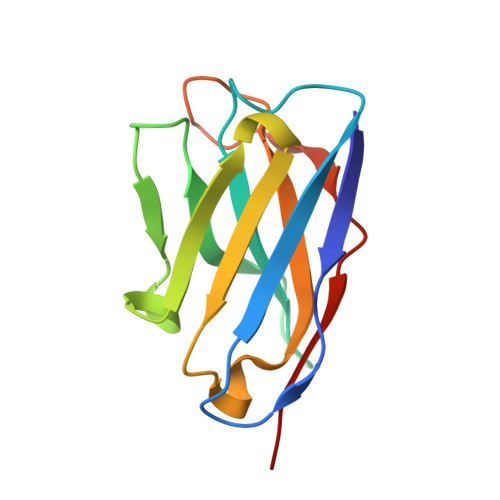
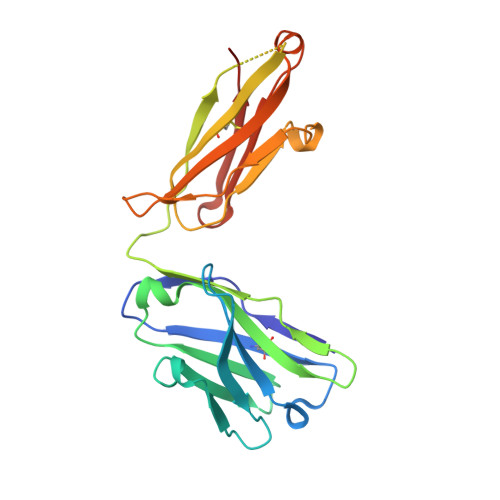
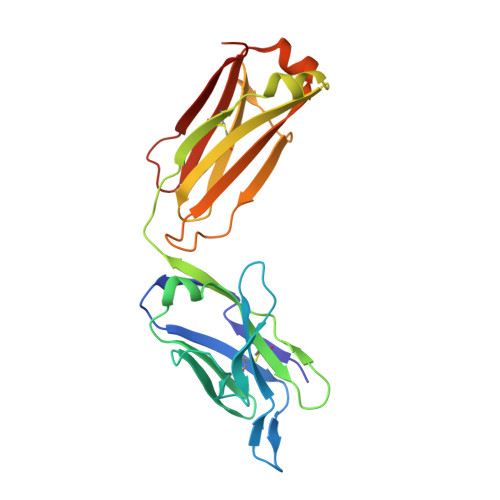
Structural Basis of Enhanced Crystallizability Induced by a Molecular Chaperone for Antibody Antigen-Binding Fragments.
Ereno-Orbea, J., Sicard, T., Cui, H., Carson, J., Hermans, P., Julien, J.P.(2018) J Mol Biol 430: 322-336
- PubMed: 29277294
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.12.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ANA, 6AND, 6ANI - PubMed Abstract:
Monoclonal antibodies constitute one of the largest groups of drugs to treat cancers and immune disorders, and are guiding the design of vaccines against infectious diseases. Fragments antigen-binding (Fabs) have been preferred over monoclonal antibodies for the structural characterization of antibody-antigen complexes due to their relatively low flexibility. Nonetheless, Fabs often remain challenging to crystallize because of the surface characteristics of complementary determining regions and the residual flexibility in the hinge region between the variable and constant domains. Here, we used a variable heavy-chain (V H H) domain specific for the human kappa light chain to assist in the structure determination of three therapeutic Fabs that were recalcitrant to crystallization on their own. We show that this ligand alters the surface properties of the antibody-ligand complex and lowers its aggregation temperature to favor crystallization. The V H H crystallization chaperone also restricts the flexible hinge of Fabs to a narrow range of angles, and so independently of the variable region. Our findings contribute a valuable approach to antibody structure determination and provide biophysical insight into the principles that govern the crystallization of macromolecules.
Organizational Affiliation:
Program in Molecular Medicine, The Hospital for Sick Children Research Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada M5G 0A4.