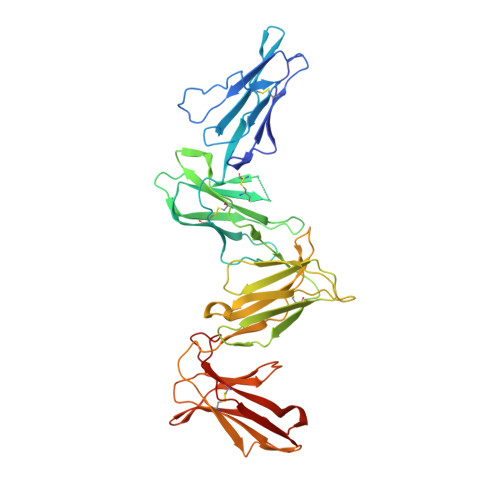
Structures of the four Ig-like domain LILRB2 and the four-domain LILRB1 and HLA-G1 complex.
Wang, Q., Song, H., Cheng, H., Qi, J., Nam, G., Tan, S., Wang, J., Fang, M., Shi, Y., Tian, Z., Cao, X., An, Z., Yan, J., Gao, G.F.(2019) Cell Mol Immunol
- PubMed: 31273318
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0258-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6AED, 6AEE - PubMed Abstract:
Leukocyte immunoglobulin (Ig)-like receptors (LILRs), also known as CD85 and immunoglobulin-like transcripts (ILTs), play pivotal roles in regulating immune responses. These receptors define an immune checkpoint that immune therapy can target. Through cis or trans interactions with human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-G, the two most abundantly expressed inhibitory LILRs, LILRB1, and LILRB2 (LILRB1/2, also known as CD85j/d and ILT2/4), are involved in immunotolerance in pregnancy and transplantation, autoimmune diseases, and immune evasion by tumors. Although the discrete domains of LILRB1/2 are clear, the assembly mode of the four extracellular Ig-like domains (D1, D2, D3, and D4) remains unknown. Previous data indicate that D1D2 is responsible for binding to HLA class I (HLA-I), but the roles of D3D4 are still unclear. Here, we determined the crystal structure of the four Ig-like domain LILRB2 and four-domain LILRB1 in complex with HLA-G1. The angles between adjacent domains and the staggered assembly of the four domains suggest limited flexibility and limited plasticity of the receptors during ligand binding. The complex structure of four-domain LILRB1 and HLA-G1 supports the model that D1D2 is responsible for HLA-I binding, while D3D4 acts as a scaffold. Accordingly, cis and trans binding models for HLA-I binding to LILRB1/2 are proposed. The geometries of LILRB1/2 in complex with dimeric and monomeric HLA-G1 suggest the accessibility of the dimeric receptor, which in turn, transduces more inhibitory signals. The assembly of LILRB1/2 and its binding to HLA-G1 could aid in the design of immune regulators and benefit immune interference.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Microbial Physiological and Metabolic Engineering, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100101, Beijing, China. wangqihui@im.ac.cn.