MORF9 increases the RNA-binding activity of PLS-type pentatricopeptide repeat protein in plastid RNA editing
Yan, J., Zhang, Q., Guan, Z., Wang, Q., Li, L., Ruan, F., Lin, R., Zou, T., Yin, P.(2017) Nat Plants 3: 17037-17037
- PubMed: 28394309
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2017.37
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
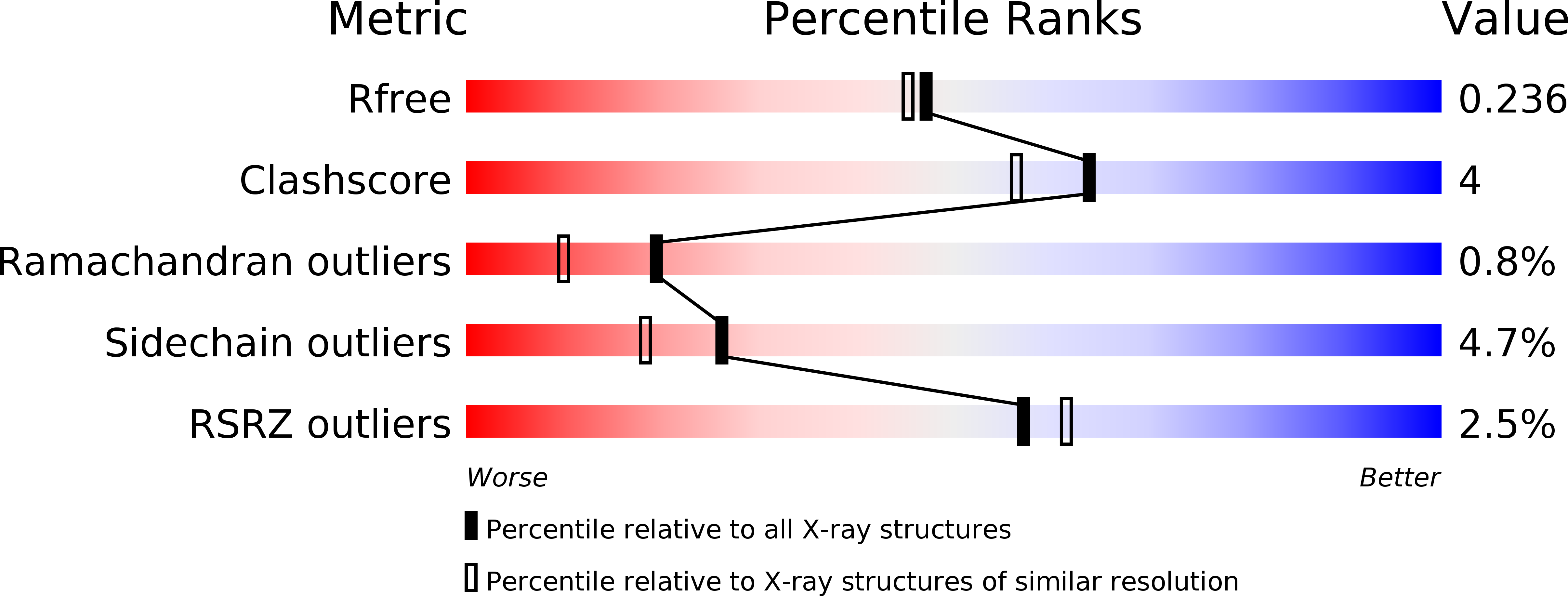
5GI0, 5IWW, 5IZW - PubMed Abstract:
RNA editing is a post-transcriptional process that modifies the genetic information on RNA molecules. In flowering plants, RNA editing usually alters cytidine to uridine in plastids and mitochondria. The PLS-type pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) protein and the multiple organellar RNA editing factor (MORF, also known as RNA editing factor interacting protein (RIP)) are two types of key trans-acting factors involved in this process. However, how they cooperate with one another remains unclear. Here, we have characterized the interactions between a designer PLS-type PPR protein (PLS) 3 PPR and MORF9, and found that RNA-binding activity of (PLS) 3 PPR is drastically increased on MORF9 binding. We also determined the crystal structures of (PLS) 3 PPR, MORF9 and the (PLS) 3 PPR-MORF9 complex. MORF9 binding induces significant compressed conformational changes of (PLS) 3 PPR, revealing the molecular mechanisms by which MORF9-bound (PLS) 3 PPR has increased RNA-binding activity. Similarly, increased RNA-binding activity is observed for the natural PLS-type PPR protein, LPA66, in the presence of MORF9. These findings significantly expand our understanding of MORF function in plant organellar RNA editing.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement and National Centre of Plant Gene Research, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China.