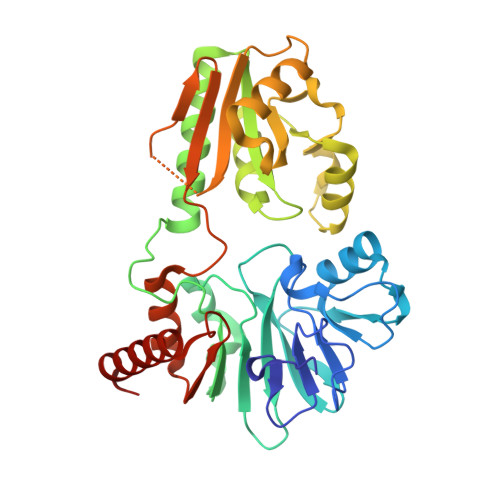
The Structures of the Snm1A and Snm1B/Apollo Nuclease Domains Reveal a Potential Basis for Their Distinct DNA Processing Activities.
Allerston, C.K., Lee, S.Y., Newman, J.A., Schofield, C.J., Mchugh, P.J., Gileadi, O.(2015) Nucleic Acids Res 43: 11047
- PubMed: 26582912
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1256
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
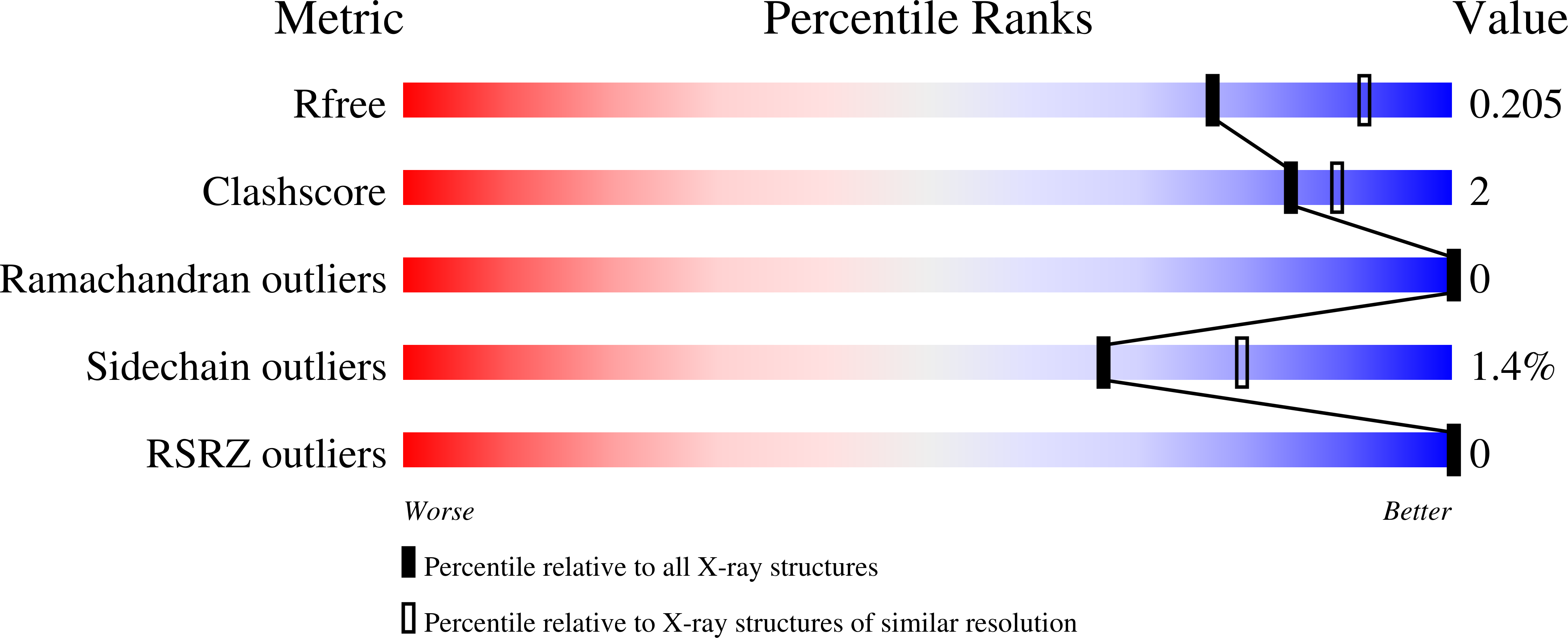
5AHO, 5AHR - PubMed Abstract:
The human SNM1A and SNM1B/Apollo proteins are members of an extended family of eukaryotic nuclease containing a motif related to the prokaryotic metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) fold. SNM1A is a key exonuclease during replication-dependent and transcription-coupled interstrand crosslink repair, while SNM1B/Apollo is required for maintaining telomeric overhangs. Here, we report the crystal structures of SNM1A and SNM1B at 2.16 Å. While both proteins contain a typical MBL-β-CASP domain, a region of positive charge surrounds the active site of SNM1A, which is absent in SNM1B and explains the greater apparent processivity of SNM1A. The structures of both proteins also reveal a putative, wide DNA-binding groove. Extensive mutagenesis of this groove, coupled with detailed biochemical analysis, identified residues that did not impact on SNM1A catalytic activity, but drastically reduced its processivity. Moreover, we identified a key role for this groove for efficient digestion past DNA interstrand crosslinks, facilitating the key DNA repair reaction catalysed by SNM1A. Together, the architecture and dimensions of this groove, coupled to the surrounding region of high positive charge, explain the remarkable ability of SNM1A to accommodate and efficiently digest highly distorted DNA substrates, such as those containing DNA lesions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Genomics Consortium, Old Road Campus Research Building, Roosevelt Drive, University of Oxford, Oxford OX3 7DQ, UK.