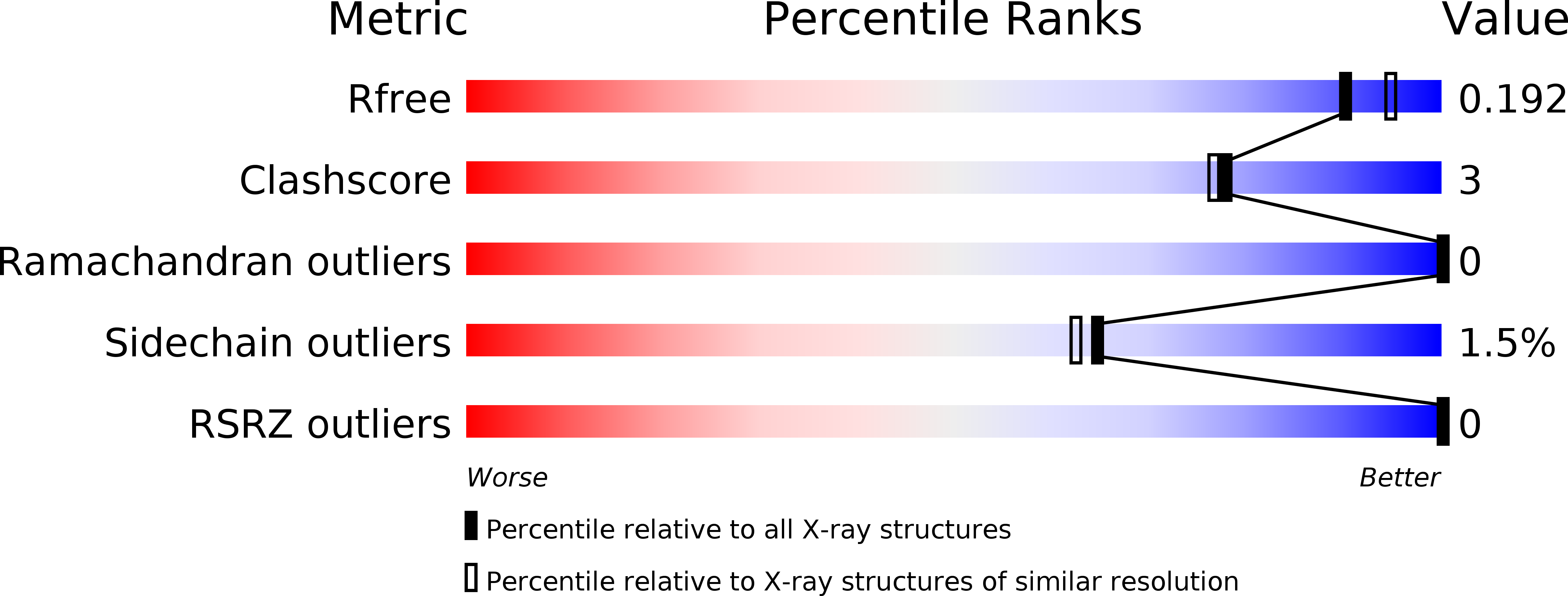
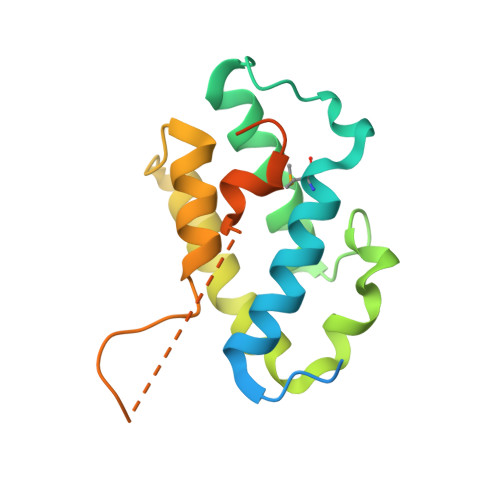
Diverse mechanisms of metaeffector activity in an intracellular bacterial pathogen, Legionella pneumophila.
Urbanus, M.L., Quaile, A.T., Stogios, P.J., Morar, M., Rao, C., Di Leo, R., Evdokimova, E., Lam, M., Oatway, C., Cuff, M.E., Osipiuk, J., Michalska, K., Nocek, B.P., Taipale, M., Savchenko, A., Ensminger, A.W.(2016) Mol Syst Biol 12: 893-893
- PubMed: 27986836
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20167381
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HFV, 4RXI, 4RXV, 4XA9, 5DGG - PubMed Abstract:
Pathogens deliver complex arsenals of translocated effector proteins to host cells during infection, but the extent to which these proteins are regulated once inside the eukaryotic cell remains poorly defined. Among all bacterial pathogens, Legionella pneumophila maintains the largest known set of translocated substrates, delivering over 300 proteins to the host cell via its Type IVB, Icm/Dot translocation system. Backed by a few notable examples of effector-effector regulation in L. pneumophila, we sought to define the extent of this phenomenon through a systematic analysis of effector-effector functional interaction. We used Saccharomyces cerevisiae, an established proxy for the eukaryotic host, to query > 108,000 pairwise genetic interactions between two compatible expression libraries of ~330 L. pneumophila-translocated substrates. While capturing all known examples of effector-effector suppression, we identify fourteen novel translocated substrates that suppress the activity of other bacterial effectors and one pair with synergistic activities. In at least nine instances, this regulation is direct-a hallmark of an emerging class of proteins called metaeffectors, or "effectors of effectors". Through detailed structural and functional analysis, we show that metaeffector activity derives from a diverse range of mechanisms, shapes evolution, and can be used to reveal important aspects of each cognate effector's function. Metaeffectors, along with other, indirect, forms of effector-effector modulation, may be a common feature of many intracellular pathogens-with unrealized potential to inform our understanding of how pathogens regulate their interactions with the host cell.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada.