Conformational changes in the capsid of a calicivirus upon interaction with its functional receptor
Ossiboff, R.J., Zhou, Y., Lightfoot, P.J., Prasad, B.V., Parker, J.S.(2010) J Virol 84: 5550-5564
- PubMed: 20357100
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02371-09
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
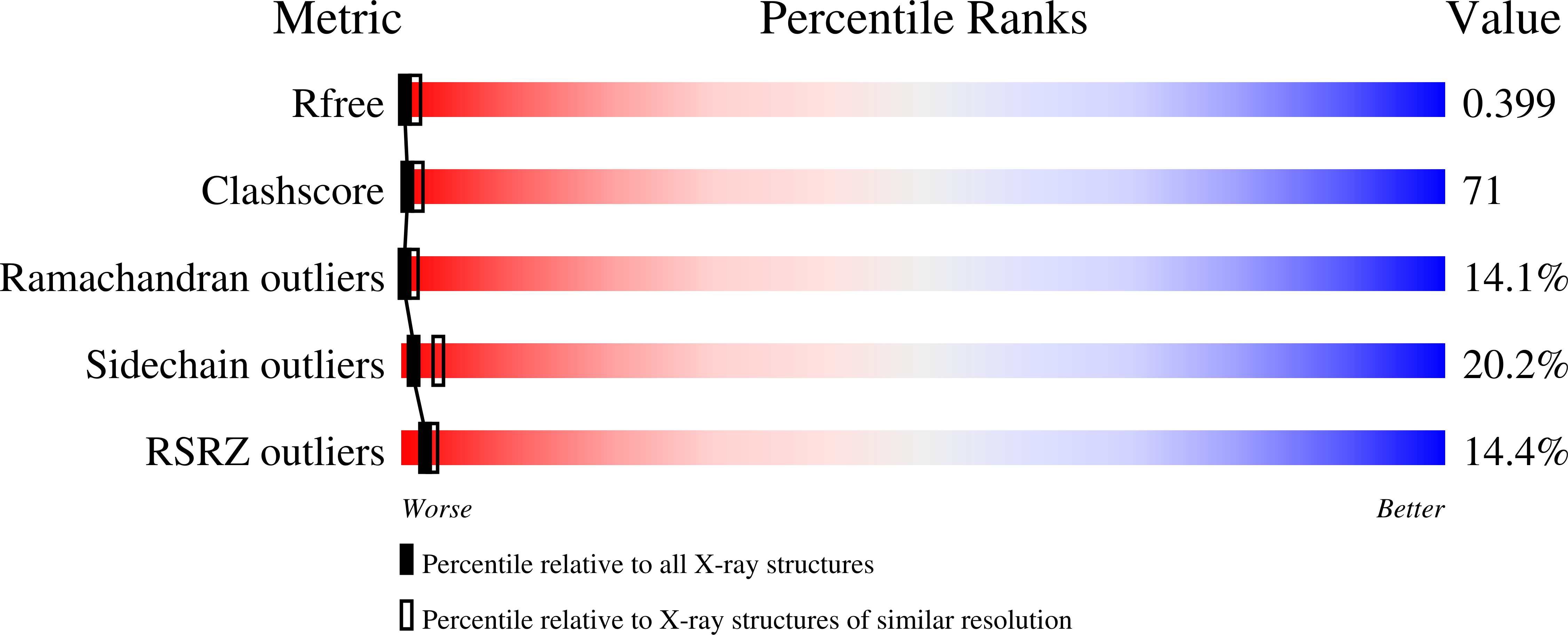
3M8L - PubMed Abstract:
Nonenveloped viral capsids are metastable structures that undergo conformational changes during virus entry that lead to interactions of the capsid or capsid fragments with the cell membrane. For members of the Caliciviridae, neither the nature of these structural changes in the capsid nor the factor(s) responsible for inducing these changes is known. Feline junctional adhesion molecule A (fJAM-A) mediates the attachment and infectious viral entry of feline calicivirus (FCV). Here, we show that the infectivity of some FCV isolates is neutralized following incubation with the soluble receptor at 37 degrees C. We used this property to select mutants resistant to preincubation with the soluble receptor. We isolated and sequenced 24 soluble receptor-resistant (srr) mutants and characterized the growth properties and receptor-binding activities of eight mutants. The location of the mutations within the capsid structure of FCV was mapped using a new 3.6-A structure of native FCV. The srr mutations mapped to the surface of the P2 domain were buried at the protruding domain dimer interface or were present in inaccessible regions of the capsid protein. Coupled with data showing that both the parental FCV and the srr mutants underwent increases in hydrophobicity upon incubation with the soluble receptor at 37 degrees C, these findings indicate that FCV likely undergoes conformational change upon interaction with its receptor. Changes in FCV capsid conformation following its interaction with fJAM-A may be important for subsequent interactions of the capsid with cellular membranes, membrane penetration, and genome delivery.
Organizational Affiliation:
Baker Institute for Animal Health, College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell University, Hungerford Hill Road, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA.