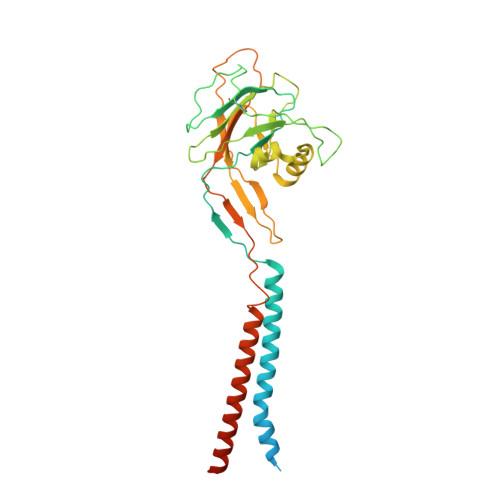
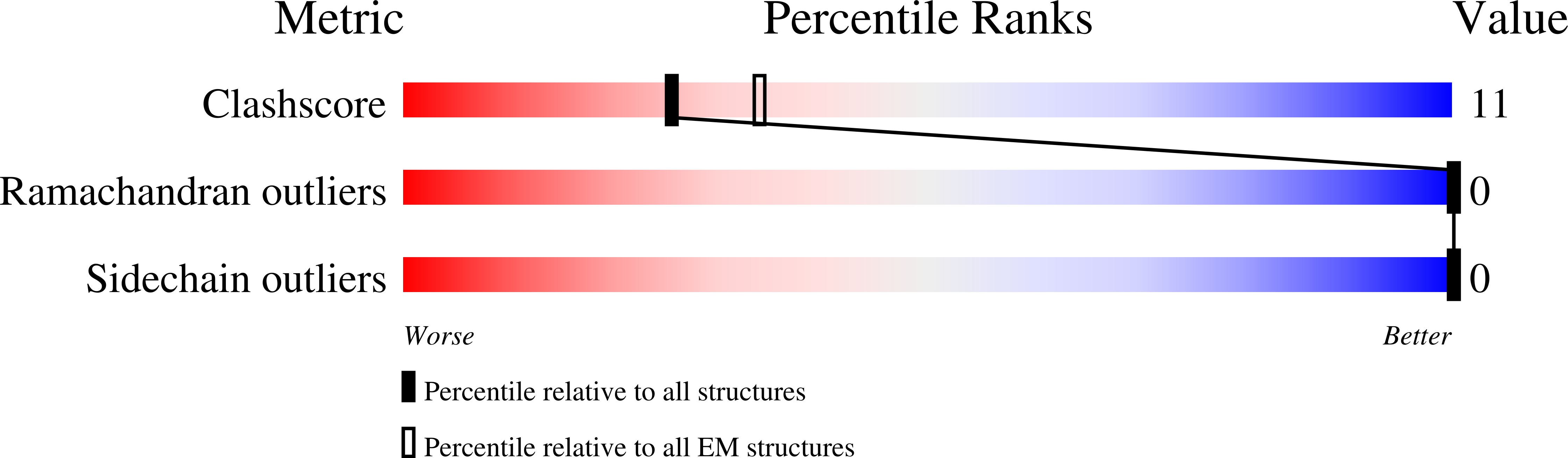Structures and pH-sensing mechanism of the proton-activated chloride channel.
Ruan, Z., Osei-Owusu, J., Du, J., Qiu, Z., Lu, W.(2020) Nature 588: 350-354
- PubMed: 33149300
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2875-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JNA, 7JNC - PubMed Abstract:
The proton-activated chloride channel (PAC) is active across a wide range of mammalian cells and is involved in acid-induced cell death and tissue injury 1-3 . PAC has recently been shown to represent a novel and evolutionarily conserved protein family 4,5 . Here we present two cryo-electron microscopy structures of human PAC in a high-pH resting closed state and a low-pH proton-bound non-conducting state. PAC is a trimer in which each subunit consists of a transmembrane domain (TMD), which is formed of two helices (TM1 and TM2), and an extracellular domain (ECD). Upon a decrease of pH from 8 to 4, we observed marked conformational changes in the ECD-TMD interface and the TMD. The rearrangement of the ECD-TMD interface is characterized by the movement of the histidine 98 residue, which is, after acidification, decoupled from the resting position and inserted into an acidic pocket that is about 5 Å away. Within the TMD, TM1 undergoes a rotational movement, switching its interaction partner from its cognate TM2 to the adjacent TM2. The anion selectivity of PAC is determined by the positively charged lysine 319 residue on TM2, and replacing lysine 319 with a glutamate residue converts PAC to a cation-selective channel. Our data provide a glimpse of the molecular assembly of PAC, and a basis for understanding the mechanism of proton-dependent activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Van Andel Institute, Grand Rapids, MI, USA.