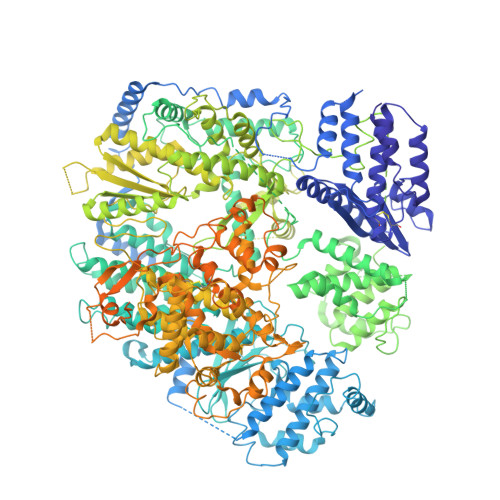
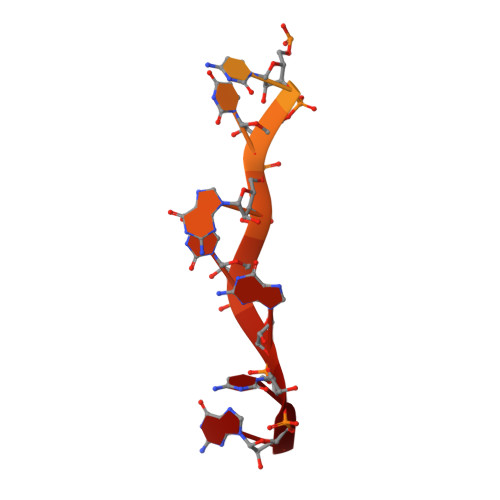
Structural insight into arenavirus replication machinery.
Peng, R., Xu, X., Jing, J., Wang, M., Peng, Q., Liu, S., Wu, Y., Bao, X., Wang, P., Qi, J., Gao, G.F., Shi, Y.(2020) Nature 579: 615-619
- PubMed: 32214249
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2114-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
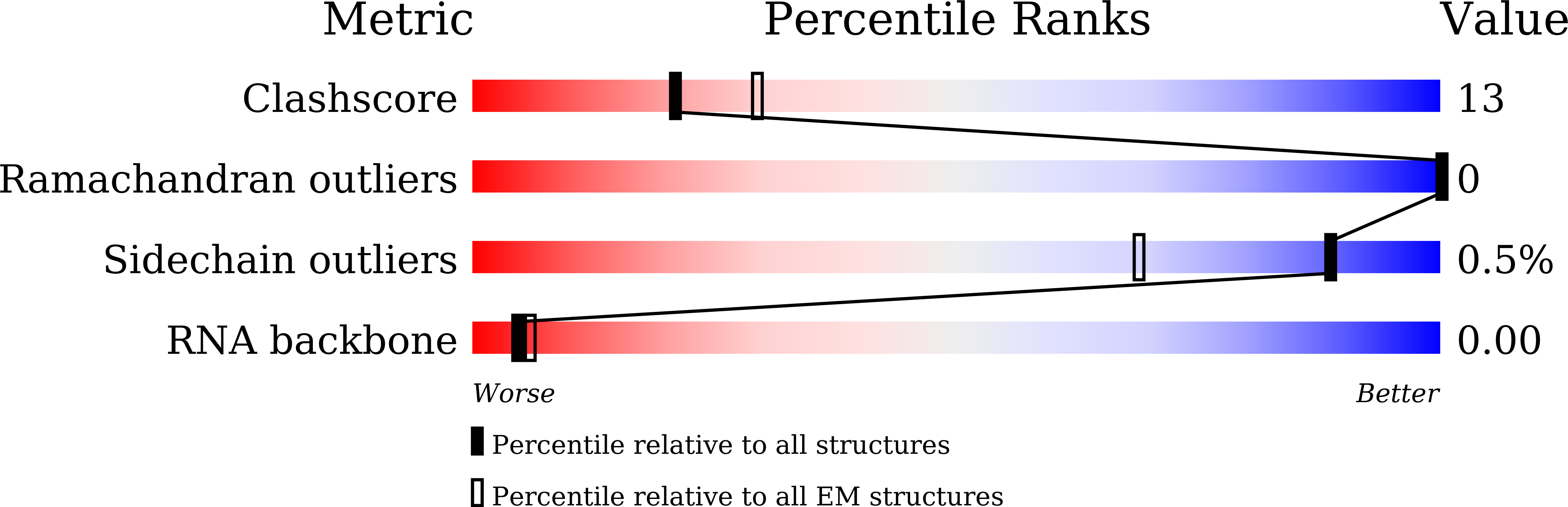
6KLC, 6KLD, 6KLE, 6KLH - PubMed Abstract:
Arenaviruses can cause severe haemorrhagic fever and neurological diseases in humans and other animals, exemplified by Lassa mammarenavirus, Machupo mammarenavirus and lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, posing great threats to public health 1-4 . These viruses encode a large multi-domain RNA-dependent RNA polymerase for transcription and replication of the viral genome 5 . Viral polymerases are one of the leading antiviral therapeutic targets. However, the structure of arenavirus polymerase is not yet known. Here we report the near-atomic resolution structures of Lassa and Machupo virus polymerases in both apo and promoter-bound forms. These structures display a similar overall architecture to influenza virus and bunyavirus polymerases but possess unique local features, including an arenavirus-specific insertion domain that regulates the polymerase activity. Notably, the ordered active site of arenavirus polymerase is inherently switched on, without the requirement for allosteric activation by 5'-viral RNA, which is a necessity for both influenza virus and bunyavirus polymerases 6,7 . Moreover, dimerization could facilitate the polymerase activity. These findings advance our understanding of the mechanism of arenavirus replication and provide an important basis for developing antiviral therapeutics.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.