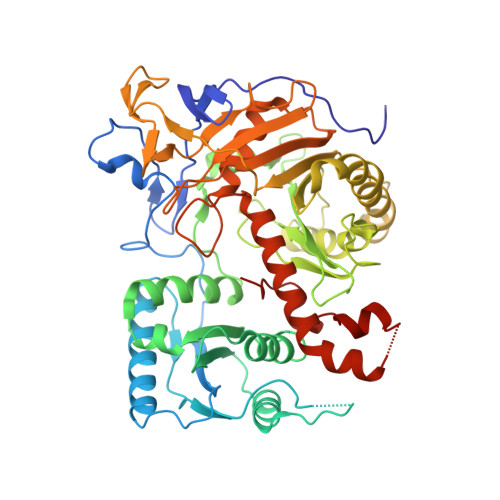
Structural and functional analyses reveal the contributions of the C- and N-lobes of Argonaute protein to selectivity of RNA target cleavage.
Dayeh, D.M., Kruithoff, B.C., Nakanishi, K.(2018) J Biol Chem 293: 6308-6325
- PubMed: 29519815
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.001051
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5THE - PubMed Abstract:
Some gene transcripts have cellular functions as regulatory noncoding RNAs. For example, ∼23-nucleotide (nt)-long siRNAs are loaded into Argonaute proteins. The resultant ribonucleoprotein assembly, the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), cleaves RNAs that are extensively base-paired with the loaded siRNA. To date, base complementarity is recognized as the major determinant of specific target cleavage (or slicing), but little is known about how Argonaute inspects base pairing before cleavage. A hallmark of Argonaute proteins is their bilobal structure, but despite the significance of this structure for curtailing slicing activity against mismatched targets, the molecular mechanism remains elusive. Here, our structural and functional studies of a bilobed yeast Argonaute protein and its isolated catalytic C-terminal lobe (C-lobe) revealed that the C-lobe alone retains almost all properties of bilobed Argonaute: siRNA-duplex loading, passenger cleavage/ejection, and siRNA-dependent RNA cleavage. A 2.1 Å-resolution crystal structure revealed that the catalytic C-lobe mirrors the bilobed Argonaute in terms of guide-RNA recognition and that all requirements for transitioning to the catalytically active conformation reside in the C-lobe. Nevertheless, we found that in the absence of the N-terminal lobe (N-lobe), target RNAs are scanned for complementarity only at positions 5-14 on a 23-nt guide RNA before endonucleolytic cleavage, thereby allowing for some off-target cleavage. Of note, acquisition of an N-lobe expanded the range of the guide RNA strand used for inspecting target complementarity to positions 2-23. These findings offer clues to the evolution of the bilobal structure of catalytically active Argonaute proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Center for RNA Biology.