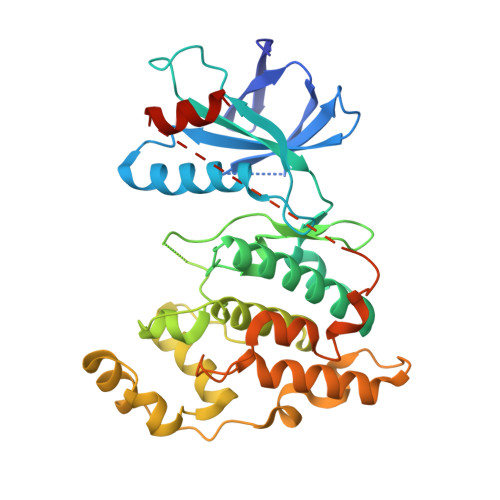
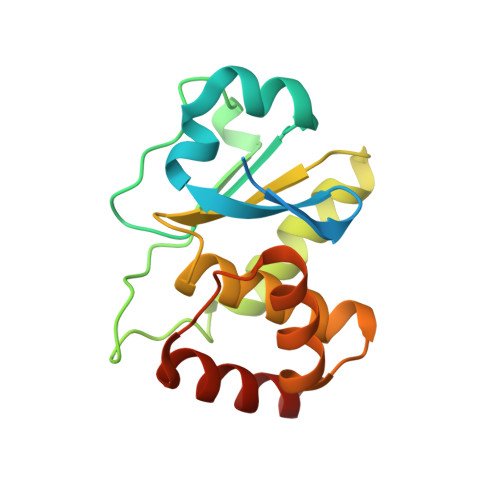
A conserved motif in JNK/p38-specific MAPK phosphatases as a determinant for JNK1 recognition and inactivation.
Liu, X., Zhang, C.S., Lu, C., Lin, S.C., Wu, J.W., Wang, Z.X.(2016) Nat Commun 7: 10879-10879
- PubMed: 26988444
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10879
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4YR8 - PubMed Abstract:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), important in a large array of signalling pathways, are tightly controlled by a cascade of protein kinases and by MAPK phosphatases (MKPs). MAPK signalling efficiency and specificity is modulated by protein-protein interactions between individual MAPKs and the docking motifs in cognate binding partners. Two types of docking interactions have been identified: D-motif-mediated interaction and FXF-docking interaction. Here we report the crystal structure of JNK1 bound to the catalytic domain of MKP7 at 2.4-Å resolution, providing high-resolution structural insight into the FXF-docking interaction. The (285)FNFL(288) segment in MKP7 directly binds to a hydrophobic site on JNK1 that is near the MAPK insertion and helix αG. Biochemical studies further reveal that this highly conserved structural motif is present in all members of the MKP family, and the interaction mode is universal and critical for the MKP-MAPK recognition and biological function.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Protein Science, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.