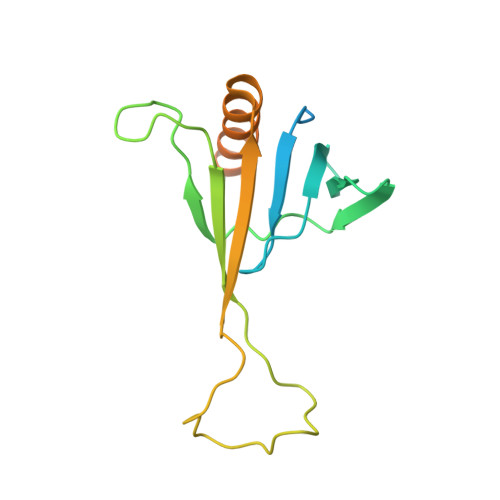
ICln159 folds into a pleckstrin homology domain-like structure. Interaction with kinases and the splicing factor LSm4
Schedlbauer, A., Gandini, R., Garavaglia, M.L., Saino, S., Gschwentner, M., Sarg, B., Lindner, H., Jakab, M., Ritter, M., Bazzini, C., Botta, G., Meyer, G., Kontaxis, G., Tilly, B.C., Konrat, R., Paulmichl, M.(2005) J Biol Chem 280: 31276-31282
- PubMed: 15905169
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M500541200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ZYI - PubMed Abstract:
ICln is a multifunctional protein involved in regulatory mechanisms as different as membrane ion transport and RNA splicing. The protein is water-soluble, and during regulatory volume decrease after cell swelling, it is able to migrate from the cytosol to the cell membrane. Purified, water-soluble ICln is able to insert into lipid bilayers to form ion channels. Here, we show that ICln159, a truncated ICln mutant, which is also able to form ion channels in lipid bilayers, belongs to the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain superfold family of proteins. The ICln PH domain shows unusual properties as it lacks the electrostatic surface polarization seen in classical PH domains. However, similar to many classical PH domain-containing proteins, ICln interacts with protein kinase C, and in addition, interacts with cAMP-dependent protein kinase and cGMP-dependent protein kinase type II but not cGMP-dependent protein kinase type Ibeta. A major phosphorylation site for all three kinases is Ser-45 within the ICln PH domain. Furthermore, ICln159 interacts with LSm4, a protein involved in splicing and mRNA degradation, suggesting that the ICln159 PH domain may serve as a protein-protein interaction platform.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physiology and Medical Physics, Innsbruck Medical University, Fritz-Pregl Strasse 3, A-6020 Innsbruck, Austria.