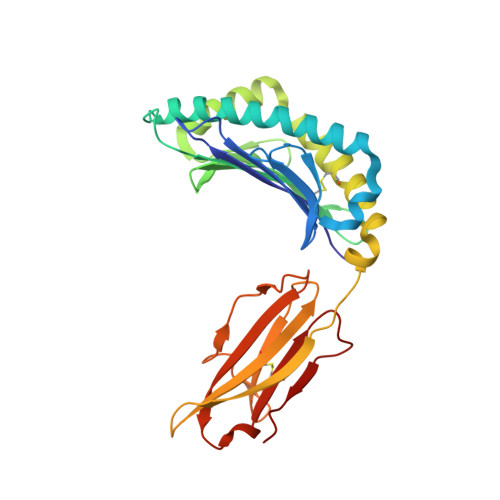
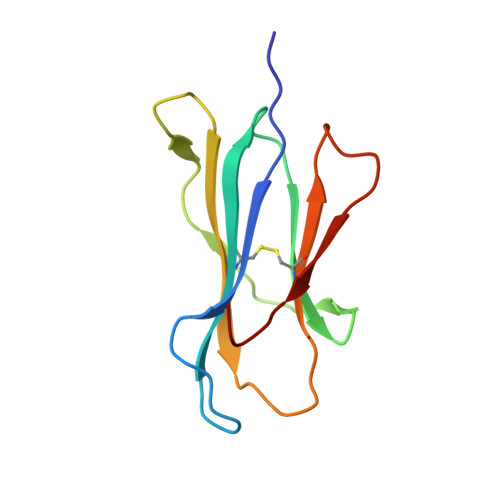
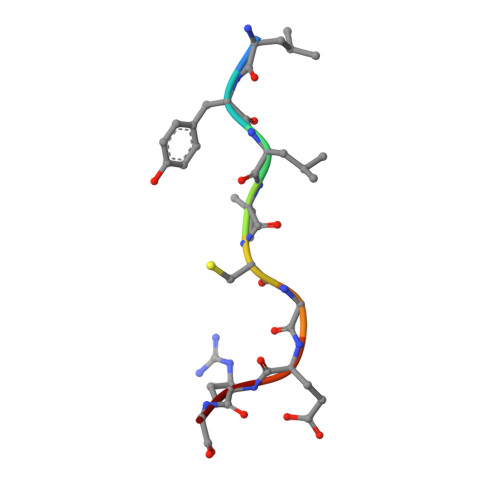
Distortion of the Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Binding Groove to Accommodate an Insulin-derived 10-Mer Peptide.
Motozono, C., Pearson, J.A., De Leenheer, E., Rizkallah, P.J., Beck, K., Trimby, A., Sewell, A.K., Wong, F.S., Cole, D.K.(2015) J Biol Chem 290: 18924-18933
- PubMed: 26085090
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.622522
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4WDI, 4Z76, 4Z78 - PubMed Abstract:
The non-obese diabetic mouse model of type 1 diabetes continues to be an important tool for delineating the role of T-cell-mediated destruction of pancreatic β-cells. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms that enable this disease pathway. We show that insulin reactivity by a CD8(+) T-cell clone, known to induce type 1 diabetes, is characterized by weak T-cell antigen receptor binding to a relatively unstable peptide-MHC. The structure of the native 9- and 10-mer insulin epitopes demonstrated that peptide residues 7 and 8 form a prominent solvent-exposed bulge that could potentially be the main focus of T-cell receptor binding. The C terminus of the peptide governed peptide-MHC stability. Unexpectedly, we further demonstrate a novel mode of flexible peptide presentation in which the MHC peptide-binding groove is able to "open the back door" to accommodate extra C-terminal peptide residues.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Division of Infection and Immunity and the Department of Immunology, Kinki University School of Medicine, Osaka 589-8511, Japan, and.