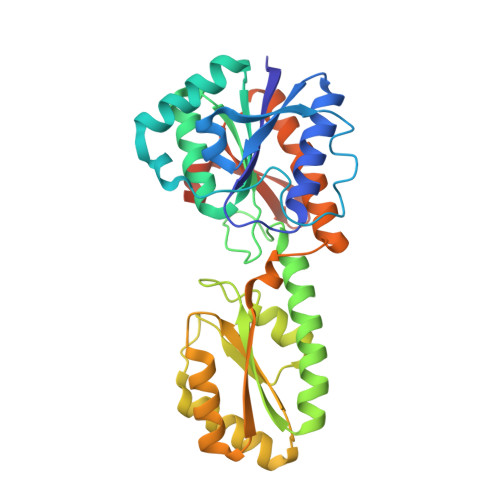
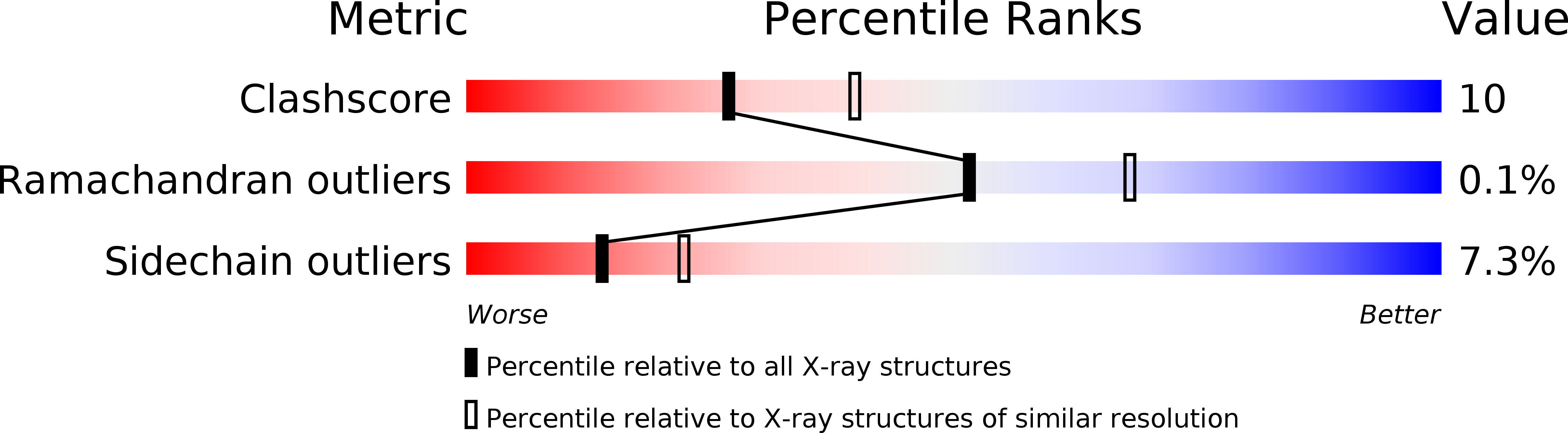Crystal structure of unliganded phosphofructokinase from Escherichia coli.
Rypniewski, W.R., Evans, P.R.(1989) J Mol Biol 207: 805-821
- PubMed: 2527305
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(89)90246-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2PFK - PubMed Abstract:
In an attempt to characterize the mechanism of co-operativity in the allosteric enzyme phosphofructokinase from Escherichia coli, crystals were grown in the absence of activating ligands. The crystal structure was determined to a resolution of 2.4 A by the method of molecular replacement, using the known structure of the liganded active state as a starting model, and has been refined to a crystallographic R-factor of 0.168 for all data. Although the crystallization solution would be expected to contain the enzyme in its inactive conformation, with a low affinity for the co-operative substrate fructose 6-phosphate, the structure in these crystals does not show the change in quaternary structure seen in the inactive form of the Bacillus stearothermophilus enzyme (previously determined at low resolution), nor does it show any substantial change in the fructose 6-phosphate site from the structure seen in the liganded form. Compared to the liganded form, there are considerable changes around the allosteric effector site, including the disordering of the last 19 residues of the chain. It seems likely that the observed conformation corresponds an active unliganded form, in which the absence of ligand in the effector site induces structural changes that spread through much of the subunit, but cause only minor changes in the active site. It is not clear why the crystals should contain the enzyme in a high-affinity conformation, which presumably represents only a small fraction of the molecules in the crystallizing solution. However, this structure does identify the conformational changes involved in binding of the allosteric effectors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, England.