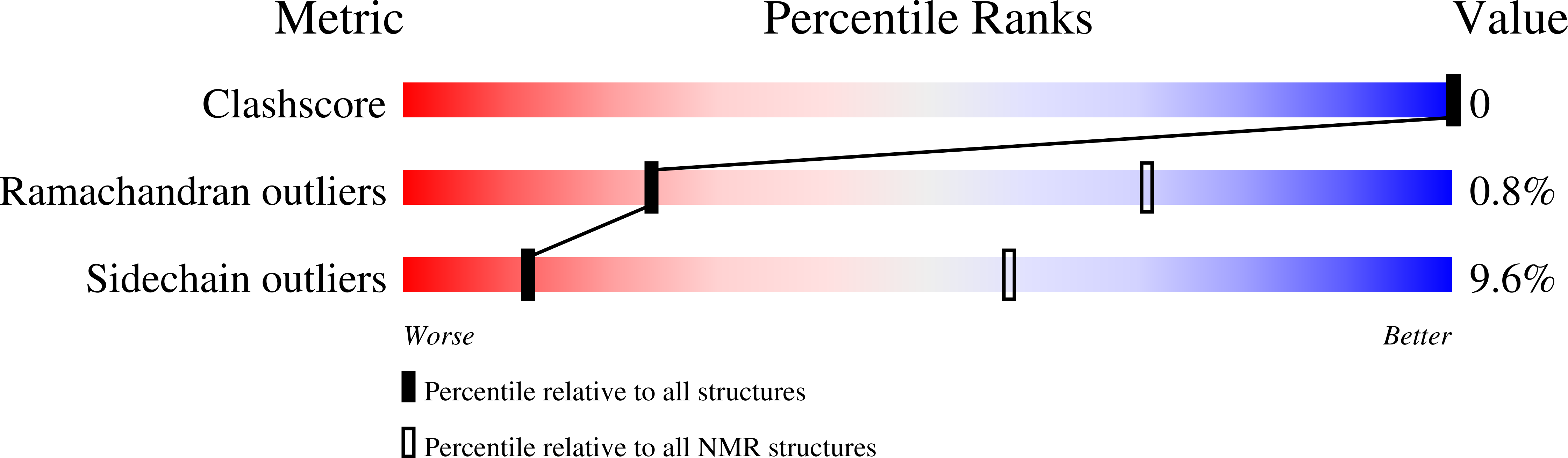Structural and mechanistic insights into unusual thiol disulfide oxidoreductase.
Garcin, E.B., Bornet, O., Elantak, L., Vita, N., Pieulle, L., Guerlesquin, F., Sebban-Kreuzer, C.(2012) J Biol Chem 287: 1688-1697
- PubMed: 22128175
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.288316
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2L6C, 2L6D - PubMed Abstract:
Cytoplasmic desulfothioredoxin (Dtrx) from the anaerobe Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough has been identified as a new member of the thiol disulfide oxidoreductase family. The active site of Dtrx contains a particular consensus sequence, CPHC, never seen in the cytoplasmic thioredoxins and generally found in periplasmic oxidases. Unlike canonical thioredoxins (Trx), Dtrx does not present any disulfide reductase activity, but it presents instead an unusual disulfide isomerase activity. We have used NMR spectroscopy to gain insights into the structure and the catalytic mechanism of this unusual Dtrx. The redox potential of Dtrx (-181 mV) is significantly less reducing than that of canonical Trx. A pH dependence study allowed the determination of the pK(a) of all protonable residues, including the cysteine and histidine residues. Thus, the pK(a) values for the thiol group of Cys(31) and Cys(34) are 4.8 and 11.3, respectively. The His(33) pK(a) value, experimentally determined for the first time, differs notably as a function of the redox states, 7.2 for the reduced state and 4.6 for the oxidized state. These data suggest an important role for His(33) in the molecular mechanism of Dtrx catalysis that is confirmed by the properties of mutant DtrxH33G protein. The NMR structure of Dtrx shows a different charge repartition compared with canonical Trx. The results presented are likely indicative of the involvement of this protein in the catalysis of substrates specific of the anaerobe cytoplasm of DvH. The study of Dtrx is an important step toward revealing the molecular details of the thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase catalytic mechanism.
Organizational Affiliation:
IMR, IFR88, CNRS, Aix-Marseille Université, Marseille 13402, France.