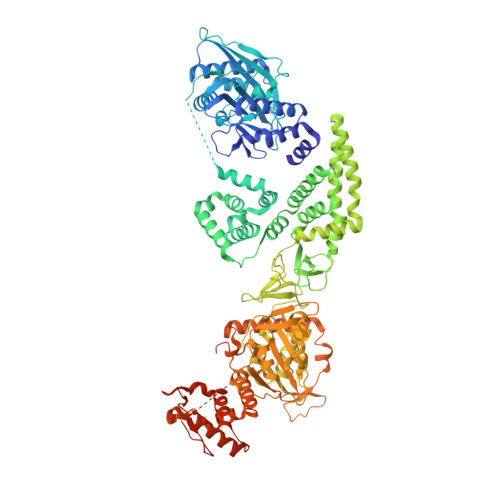
Structures and implications of the C962R protein of African swine fever virus.
Shao, Z., Su, S., Yang, J., Zhang, W., Gao, Y., Zhao, X., Zhang, Y., Shao, Q., Cao, C., Li, H., Liu, H., Zhang, J., Lin, J., Ma, J., Gan, J.(2023) Nucleic Acids Res 51: 9475-9490
- PubMed: 37587714
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad677
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8IQB, 8IQC, 8IQD, 8IQH, 8IQI - PubMed Abstract:
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is highly contagious and can cause lethal disease in pigs. Although it has been extensively studied in the past, no vaccine or other useful treatment against ASFV is available. The genome of ASFV encodes more than 170 proteins, but the structures and functions for the majority of the proteins remain elusive, which hindered our understanding on the life cycle of ASFV and the development of ASFV-specific inhibitors. Here, we report the structural and biochemical studies of the highly conserved C962R protein of ASFV, showing that C962R is a multidomain protein. The N-terminal AEP domain is responsible for the DNA polymerization activity, whereas the DNA unwinding activity is catalyzed by the central SF3 helicase domain. The middle PriCT2 and D5_N domains and the C-terminal Tail domain all contribute to the DNA unwinding activity of C962R. C962R preferentially works on forked DNA, and likely functions in Base-excision repair (BER) or other repair pathway in ASFV. Although it is not essential for the replication of ASFV, C962R can serve as a model and provide mechanistic insight into the replicative primase proteins from many other species, such as nitratiruptor phage NrS-1, vaccinia virus (VACV) and other viruses.
Organizational Affiliation:
Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Collaborative Innovation Center of Genetics and Development, Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200438, China.