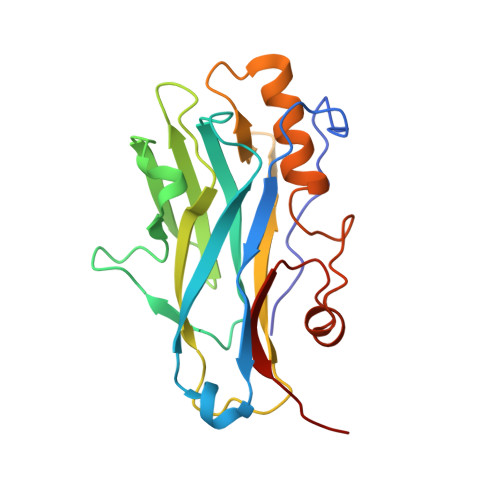
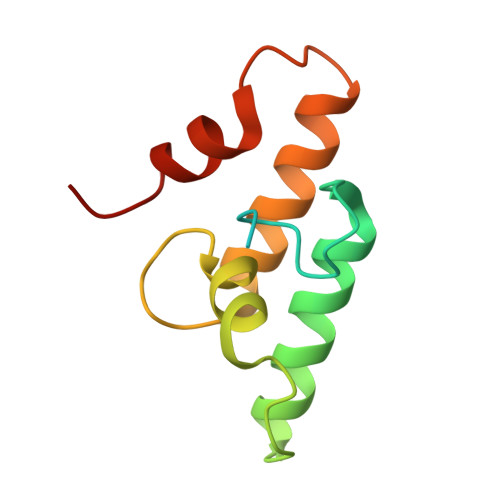
Structure-function studies can improve binding affinity of cohesin-dockerin interactions for multi-protein assemblies.
Duarte, M., Alves, V.D., Correia, M., Caseiro, C., Ferreira, L.M.A., Romao, M.J., Carvalho, A.L., Najmudin, S., Bayer, E.A., Fontes, C.M.G.A., Bule, P.(2023) Int J Biol Macromol 224: 55-67
- PubMed: 36252630
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.102
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8AJY - PubMed Abstract:
The cellulosome is an elaborate multi-enzyme structure secreted by many anaerobic microorganisms for the efficient degradation of lignocellulosic substrates. It is composed of multiple catalytic and non-catalytic components that are assembled through high-affinity protein-protein interactions between the enzyme-borne dockerin (Doc) modules and the repeated cohesin (Coh) modules present in primary scaffoldins. In some cellulosomes, primary scaffoldins can interact with adaptor and cell-anchoring scaffoldins to create structures of increasing complexity. The cellulosomal system of the ruminal bacterium, Ruminococcus flavefaciens, is one of the most intricate described to date. An unprecedent number of different Doc specificities results in an elaborate architecture, assembled exclusively through single-binding-mode type-III Coh-Doc interactions. However, a set of type-III Docs exhibits certain features associated with the classic dual-binding mode Coh-Doc interaction. Here, the structure of the adaptor scaffoldin-borne ScaH Doc in complex with the Coh from anchoring scaffoldin ScaE is described. This complex, unlike previously described type-III interactions in R. flavefaciens, was found to interact in a dual-binding mode. The key residues determining Coh recognition were also identified. This information was used to perform structure-informed protein engineering to change the electrostatic profile of the binding surface and to improve the affinity between the two modules. The results show that the nature of the residues in the ligand-binding surface plays a major role in Coh recognition and that Coh-Doc affinity can be manipulated through rational design, a key feature for the creation of designer cellulosomes or other affinity-based technologies using tailored Coh-Doc interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
CIISA-Centre for Interdisciplinary Research in Animal Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Lisbon, 1300-477 Lisbon, Portugal; Associate Laboratory for Animal and Veterinary Sciences (AL4AnimalS), 1300-477 Lisbon, Portugal.