Accelerating the design of pili-enabled living materials using an integrative technological workflow.
Huang, Y., Wu, Y., Hu, H., Tong, B., Wang, J., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Yin, Y., Dai, S., Zhao, W., An, B., Pu, J., Wang, Y., Peng, C., Li, N., Zhou, J., Tan, Y., Zhong, C.(2023) Nat Chem Biol
- PubMed: 38012344
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-023-01489-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
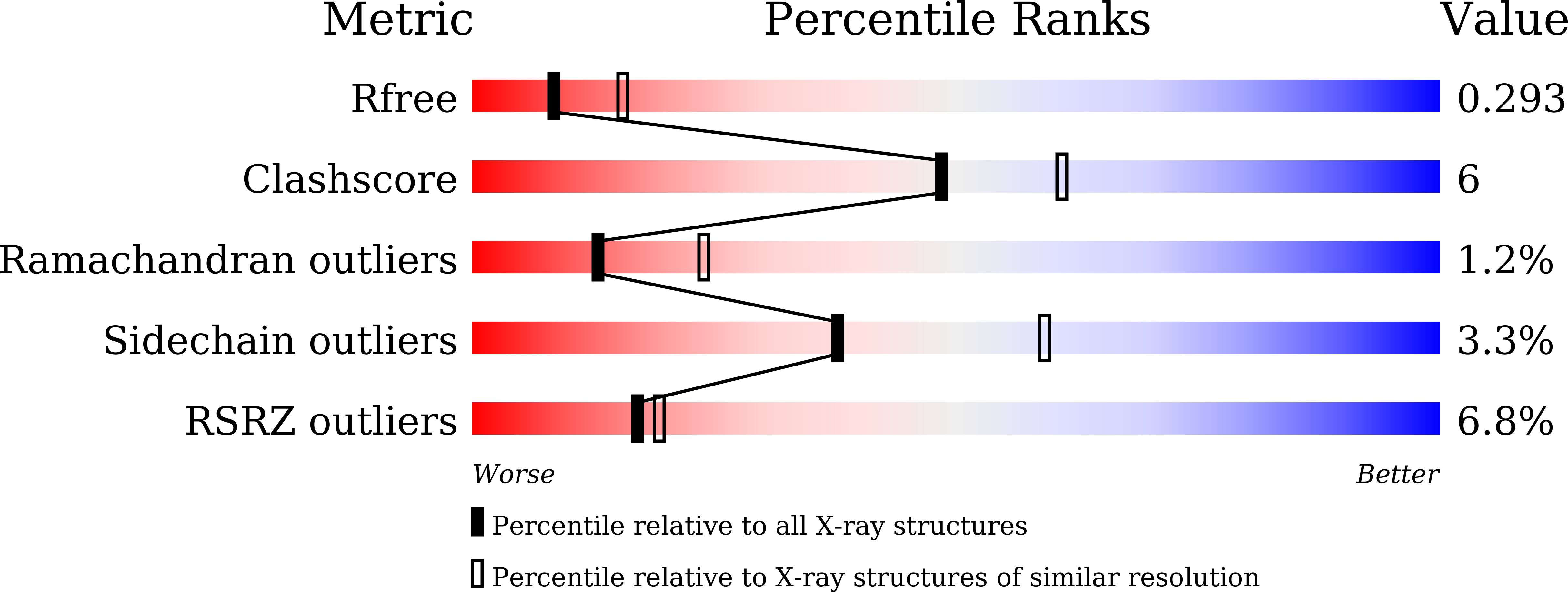
7WOI - PubMed Abstract:
Bacteria can be programmed to create engineered living materials (ELMs) with self-healing and evolvable functionalities. However, further development of ELMs is greatly hampered by the lack of engineerable nonpathogenic chassis and corresponding programmable endogenous biopolymers. Here, we describe a technological workflow for facilitating ELMs design by rationally integrating bioinformatics, structural biology and synthetic biology technologies. We first develop bioinformatics software, termed Bacteria Biopolymer Sniffer (BBSniffer), that allows fast mining of biopolymers and biopolymer-producing bacteria of interest. As a proof-of-principle study, using existing pathogenic pilus as input, we identify the covalently linked pili (CLP) biosynthetic gene cluster in the industrial workhorse Corynebacterium glutamicum. Genetic manipulation and structural characterization reveal the molecular mechanism of the CLP assembly, ultimately enabling a type of programmable pili for ELM design. Finally, engineering of the CLP-enabled living materials transforms cellulosic biomass into lycopene by coupling the extracellular and intracellular bioconversion ability.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Quantitative Synthetic Biology, Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China.