Linking the thermostability of FIP-nha (Nectria haematococca) to its structural properties.
Liu, Y., Bastiaan-Net, S., Zhang, Y., Hoppenbrouwers, T., Xie, Y., Wang, Y., Wei, X., Du, G., Zhang, H., Imam, K.M.D.S.U., Wichers, H., Li, Z.(2022) Int J Biol Macromol 213: 555-564
- PubMed: 35644318
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.05.136
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
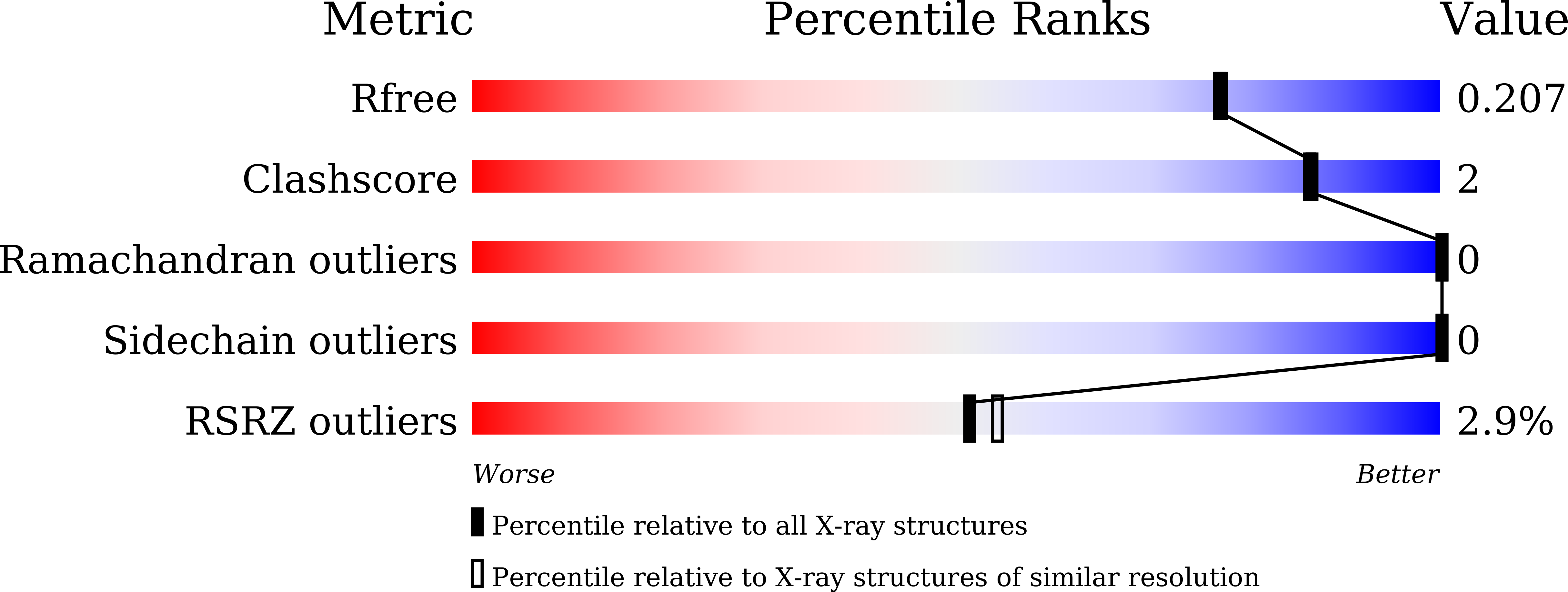
7WDL - PubMed Abstract:
Fungal immunomodulatory proteins (FIPs) have been investigated for their use as potential natural derived anti-tumor molecules. However, the stability of FIPs is critical for their preparation and storage. In this study, the correlation between thermal stability and protein structural features of rFIP-nha, with significant anti-tumor activity, has been evaluated. For comprehensive analysis, FIP-nha and its homologues FIP-gmi, FIP-fve, and LZ-8 were all recombinantly expressed in E. coli. In solution, rFIP-nha and rFIP-gmi formed tetramers; rFIP-fve and rLZ-8 appeared as dimers. Their melting temperatures were 85.1 °C, 77.8 °C, 66.5 °C, and 64.4 °C, respectively. Accordingly, their cytotoxicity was also temperature dependent. To investigate the underlying mechanism of their thermostability, we solved the crystal structure of FIP-nha. Detailed structure analysis, molecular dynamic simulation and mutagenesis studies indicated that a higher thermostability was correlated to higher oligomerization states, larger interface area, and more interactions. The structure property studies indicate that Y12, D61 and Y108 were critical for oligomerization and high thermostability of rFIP-nha, but the dimeric and tetrameric states of rFIP-nha exert similar cytotoxicity on A549 cells. Taken together, these findings reveal that thermostability of FIPs was dependent on their oligomerization state, and correlated with their cytotoxicity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Biomanufacturing and Food Engineering, Institute of Food Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Agriculture Sciences, Beijing 100193, China; Wageningen Food and Biobased Research, Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen 6708WG, the Netherlands; Laboratory of Food Chemistry, Wageningen University, Wageningen 6708WG, the Netherlands.