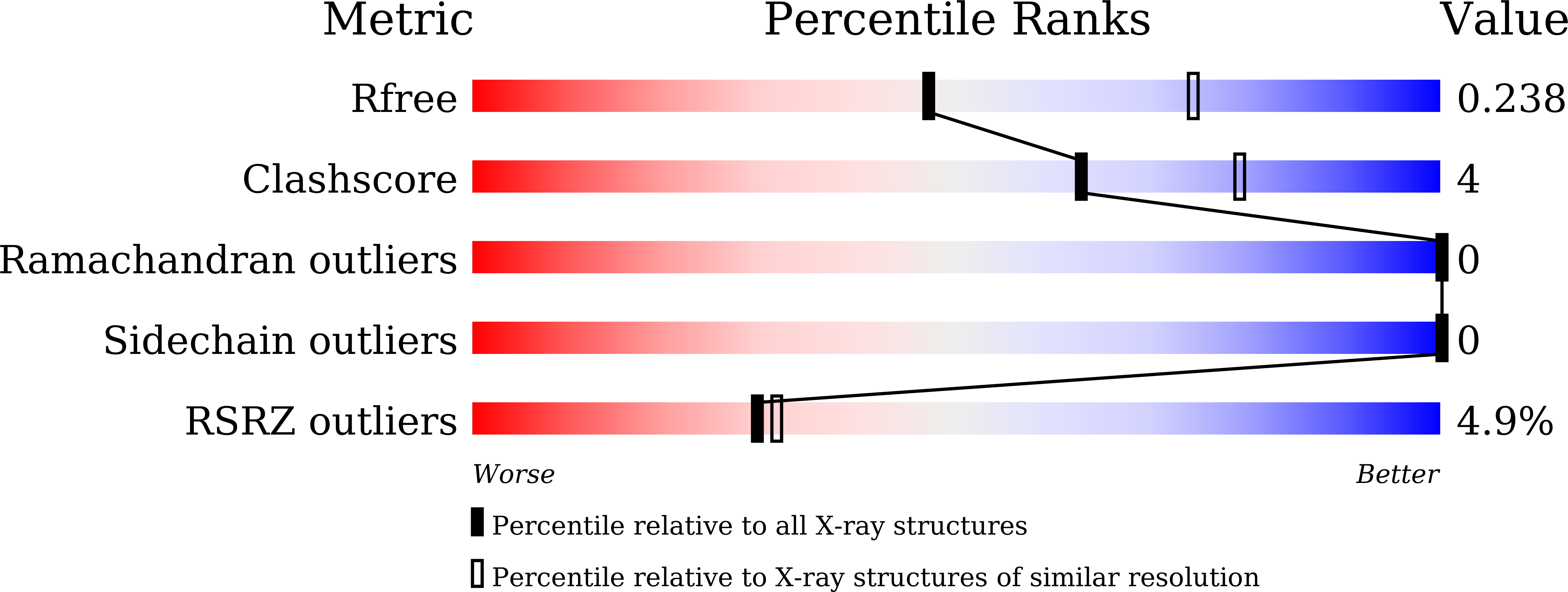
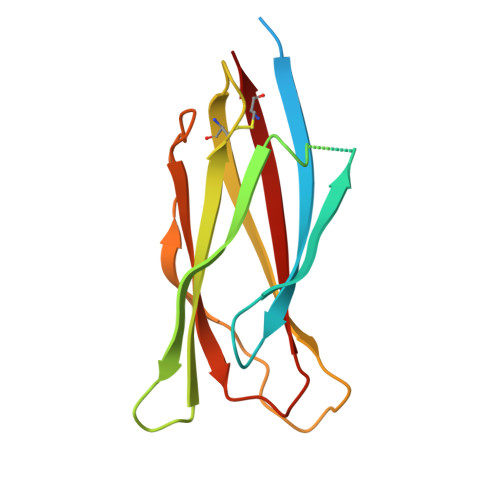
Crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of envelope protein VP37 from white spot syndrome virus reveals sulphate binding sites responsible for heparin binding.
Somsoros, W., Sangawa, T., Takebe, K., Attarataya, J., Wongprasert, K., Senapin, S., Rattanarojpong, T., Suzuki, M., Khunrae, P.(2021) J Gen Virol 102
- PubMed: 34106826
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1099/jgv.0.001611
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7DDA - PubMed Abstract:
White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) is the most virulent pathogen causing high mortality and economic loss in shrimp aquaculture and various crustaceans. Therefore, the understanding of molecular mechanisms of WSSV infection is important to develop effective therapeutics to control the spread of this viral disease. In a previous study, we found that VP37 could bind with shrimp haemocytes through the interaction between its C-terminal domain and heparin-like molecules on the shrimp cells, and this interaction can also be inhibited by sulphated galactan. In this study, we present the crystal structure of C-terminal domain of VP37 from WSSV at a resolution of 2.51 Å. The crystal structure contains an eight-stranded β-barrel fold with an antiparallel arrangement and reveals a trimeric assembly. Moreover, there are two sulphate binding sites found in the position corresponding to R213 and K257. In order to determine whether these sulphate binding sites are involved in binding of VP37 to heparin, mutagenesis was performed to replace these residues with alanine (R213A and K257A), and the Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) system was used to study the interaction of each mutated VP37 with heparin. The results showed that mutants R213A and K257A exhibited a significant loss in heparin binding activity. These findings indicated that the sites of R213 and K257 on the C-terminal domain of envelope protein VP37 are essential for binding to sulphate molecules of heparin. This study provides further insight into the structure of C-terminal domain of VP37 and it is anticipated that the structure of VP37 might be used as a guideline for development of antivirus agent targeting on the VP37 protein.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi, Bangkok 10140, Thailand.