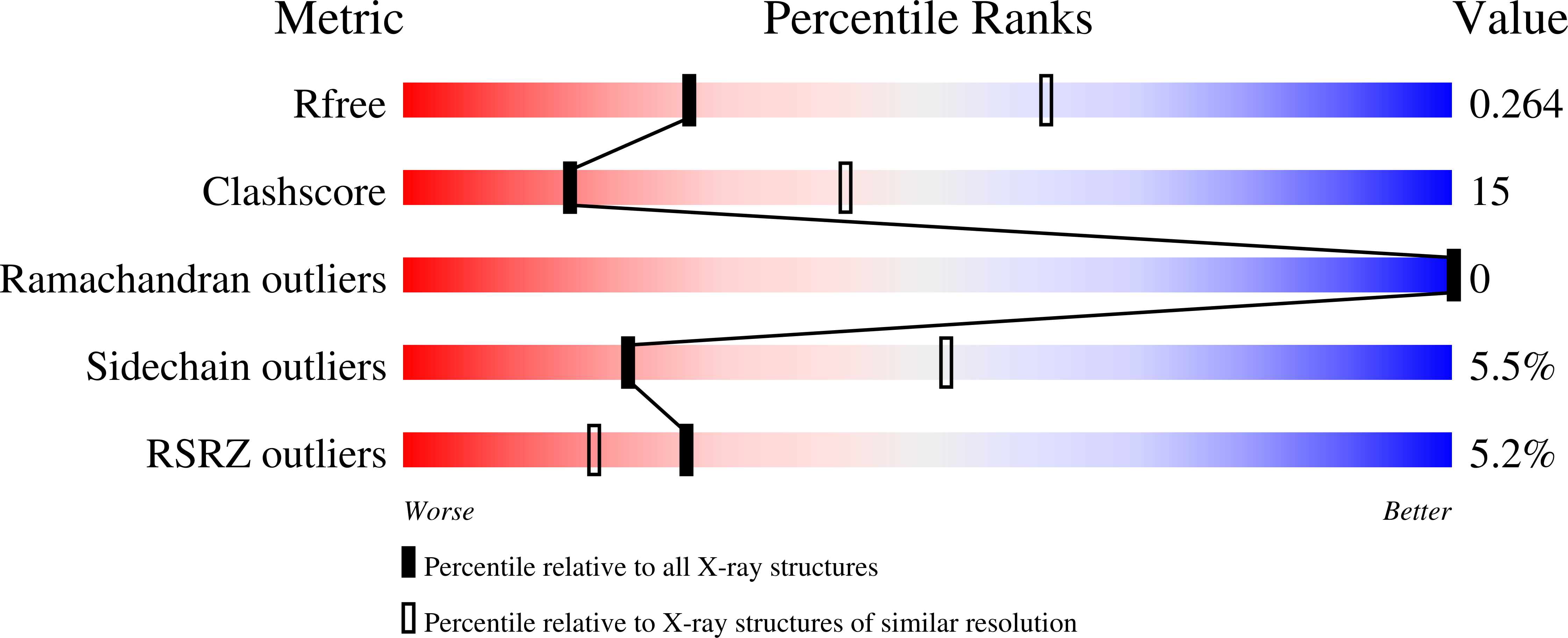
Structure, interdomain dynamics, and pH-dependent autoactivation of pro-rhodesain, the main lysosomal cysteine protease from African trypanosomes.
Johe, P., Jaenicke, E., Neuweiler, H., Schirmeister, T., Kersten, C., Hellmich, U.A.(2021) J Biol Chem 296: 100565-100565
- PubMed: 33745969
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100565
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7AVM - PubMed Abstract:
Rhodesain is the lysosomal cathepsin L-like cysteine protease of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense, the causative agent of Human African Trypanosomiasis. The enzyme is essential for the proliferation and pathogenicity of the parasite as well as its ability to overcome the blood-brain barrier of the host. Lysosomal cathepsins are expressed as zymogens with an inactivating prodomain that is cleaved under acidic conditions. A structure of the uncleaved maturation intermediate from a trypanosomal cathepsin L-like protease is currently not available. We thus established the heterologous expression of T. brucei rhodesiense pro-rhodesain in Escherichia coli and determined its crystal structure. The trypanosomal prodomain differs from nonparasitic pro-cathepsins by a unique, extended α-helix that blocks the active site and whose side-chain interactions resemble those of the antiprotozoal inhibitor K11777. Interdomain dynamics between pro- and core protease domain as observed by photoinduced electron transfer fluorescence correlation spectroscopy increase at low pH, where pro-rhodesain also undergoes autocleavage. Using the crystal structure, molecular dynamics simulations, and mutagenesis, we identify a conserved interdomain salt bridge that prevents premature intramolecular cleavage at higher pH values and may thus present a control switch for the observed pH sensitivity of proenzyme cleavage in (trypanosomal) CathL-like proteases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences, Johannes Gutenberg-University, Mainz, Germany.