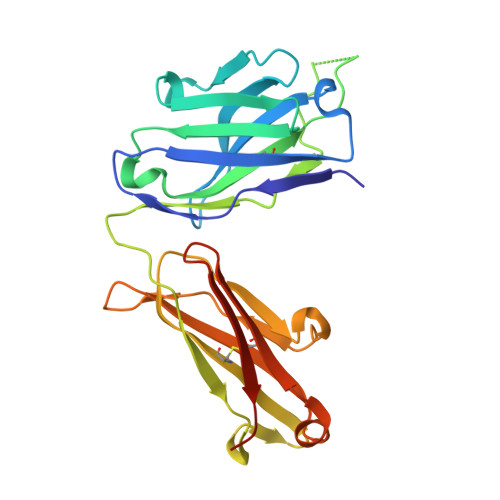
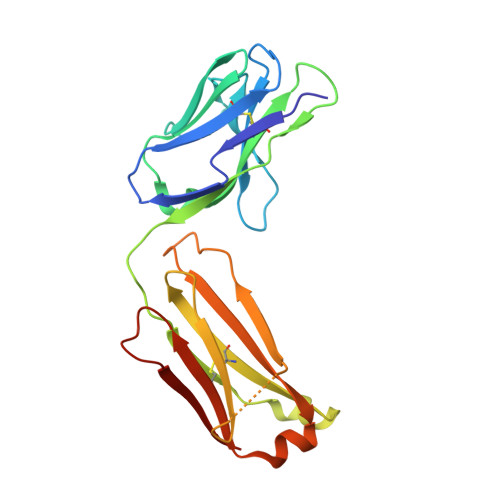
Cross-Neutralization of a SARS-CoV-2 Antibody to a Functionally Conserved Site Is Mediated by Avidity.
Liu, H., Wu, N.C., Yuan, M., Bangaru, S., Torres, J.L., Caniels, T.G., van Schooten, J., Zhu, X., Lee, C.D., Brouwer, P.J.M., van Gils, M.J., Sanders, R.W., Ward, A.B., Wilson, I.A.(2020) Immunity 53: 1272-1280.e5
- PubMed: 33242394
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.10.023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JMW, 7JMX - PubMed Abstract:
Most antibodies isolated from individuals with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are specific to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). However, COVA1-16 is a relatively rare antibody that also cross-neutralizes SARS-CoV. Here, we determined a crystal structure of the COVA1-16 antibody fragment (Fab) with the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) and negative-stain electron microscopy reconstructions with the spike glycoprotein trimer to elucidate the structural basis of its cross-reactivity. COVA1-16 binds a highly conserved epitope on the SARS-CoV-2 RBD, mainly through a long complementarity-determining region (CDR) H3, and competes with the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor because of steric hindrance rather than epitope overlap. COVA1-16 binds to a flexible up conformation of the RBD on the spike and relies on antibody avidity for neutralization. These findings, along with the structural and functional rationale for epitope conservation, provide insights for development of more universal SARS-like coronavirus vaccines and therapies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Integrative Structural and Computational Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.