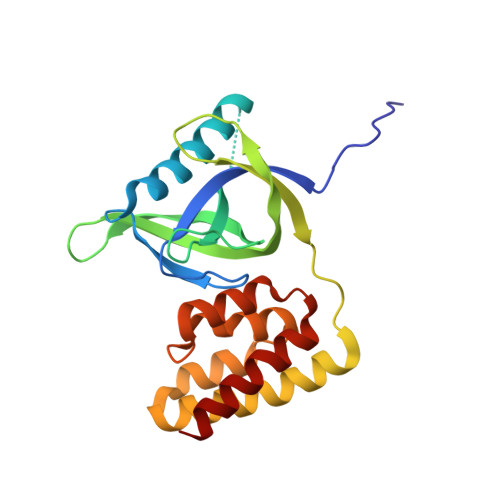
Crystal structure of the N domain of Lon protease from Mycobacterium avium complex.
Chen, X., Zhang, S., Bi, F., Guo, C., Feng, L., Wang, H., Yao, H., Lin, D.(2019) Protein Sci 28: 1720-1726
- PubMed: 31306520
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3687
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6IHG, 6VBK - PubMed Abstract:
Lon protease is evolutionarily conserved in prokaryotes and eukaryotic organelles. The primary function of Lon is to selectively degrade abnormal and certain regulatory proteins to maintain the homeostasis in vivo. Lon mainly consists of three functional domains and the N-terminal domain is required for the substrate selection and recognition. However, the precise contribution of the N-terminal domain remains elusive. Here, we determined the crystal structure of the N-terminal 192-residue construct of Lon protease from Mycobacterium avium complex at 2.4 å resolution,and measured NMR-relaxation parameters of backbones. This structure consists of two subdomains, the β-strand rich N-terminal subdomain and the five-helix bundle of C-terminal subdomain, connected by a flexible linker,and is similar to the overall structure of the N domain of Escherichia coli Lon even though their sequence identity is only 26%. The obtained NMR-relaxation parameters reveal two stabilized loops involved in the structural packing of the compact N domain and a turn structure formation. The performed homology comparison suggests that structural and sequence variations in the N domain may be closely related to the substrate selectivity of Lon variants. Our results provide the structure and dynamics characterization of a new Lon N domain, and will help to define the precise contribution of the Lon N-terminal domain to the substrate recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Biology, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China.