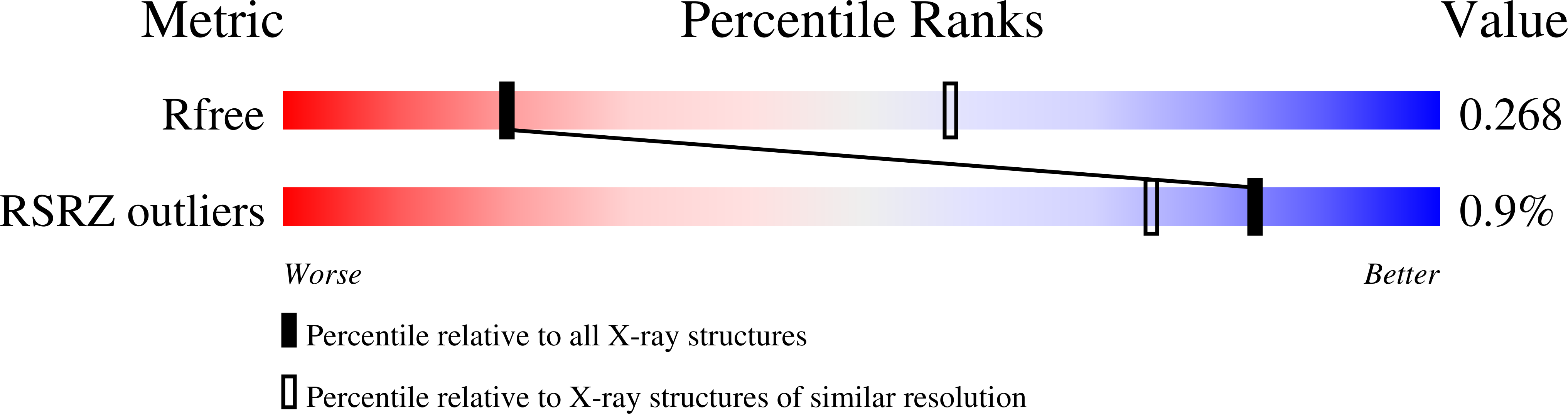Cytomegalovirus immediate-early 1 proteins form a structurally distinct protein class with adaptations determining cross-species barriers.
Schweininger, J., Scherer, M., Rothemund, F., Schilling, E.M., Worz, S., Stamminger, T., Muller, Y.A.(2021) PLoS Pathog 17: e1009863-e1009863
- PubMed: 34370791
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1009863
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6TGZ, 6TH1 - PubMed Abstract:
Restriction factors are potent antiviral proteins that constitute a first line of intracellular defense by blocking viral replication and spread. During co-evolution, however, viruses have developed antagonistic proteins to modulate or degrade the restriction factors of their host. To ensure the success of lytic replication, the herpesvirus human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) expresses the immediate-early protein IE1, which acts as an antagonist of antiviral, subnuclear structures termed PML nuclear bodies (PML-NBs). IE1 interacts directly with PML, the key protein of PML-NBs, through its core domain and disrupts the dot-like multiprotein complexes thereby abrogating the antiviral effects. Here we present the crystal structures of the human and rat cytomegalovirus core domain (IE1CORE). We found that IE1CORE domains, also including the previously characterized IE1CORE of rhesus CMV, form a distinct class of proteins that are characterized by a highly similar and unique tertiary fold and quaternary assembly. This contrasts to a marked amino acid sequence diversity suggesting that strong positive selection evolved a conserved fold, while immune selection pressure may have fostered sequence divergence of IE1. At the same time, we detected specific differences in the helix arrangements of primate versus rodent IE1CORE structures. Functional characterization revealed a conserved mechanism of PML-NB disruption, however, primate and rodent IE1 proteins were only effective in cells of the natural host species but not during cross-species infection. Remarkably, we observed that expression of HCMV IE1 allows rat cytomegalovirus replication in human cells. We conclude that cytomegaloviruses have evolved a distinct protein tertiary structure of IE1 to effectively bind and inactivate an important cellular restriction factor. Furthermore, our data show that the IE1 fold has been adapted to maximize the efficacy of PML targeting in a species-specific manner and support the concept that the PML-NBs-based intrinsic defense constitutes a barrier to cross-species transmission of HCMV.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biotechnology, Department of Biology, Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany.