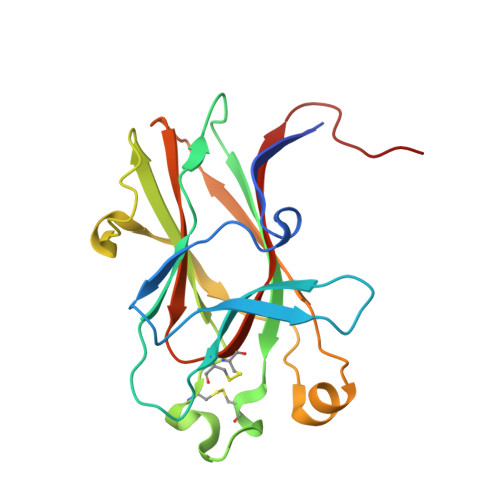
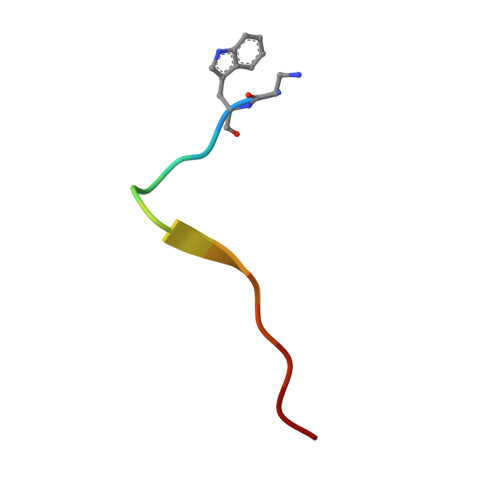
Engineering nanomolar peptide ligands that differentially modulate EphA2 receptor signaling.
Gomez-Soler, M., Petersen Gehring, M., Lechtenberg, B.C., Zapata-Mercado, E., Hristova, K., Pasquale, E.B.(2019) J Biol Chem 294: 8791-8805
- PubMed: 31015204
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.008213
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NJZ, 6NK0, 6NK1, 6NK2, 6NKP - PubMed Abstract:
The EPH receptor A2 (EphA2) tyrosine kinase plays an important role in a plethora of biological and disease processes, ranging from angiogenesis and cancer to inflammation and parasitic infections. EphA2 is therefore considered an important drug target. Two short peptides previously identified by phage display, named YSA and SWL, are widely used as EphA2-targeting agents owing to their high specificity for this receptor. However, these peptides have only modest (micromolar) potency. Lack of structural information on the binding interactions of YSA and SWL with the extracellular EphA2 ligand-binding domain (LBD) has for many years precluded structure-guided improvements. We now report the high-resolution (1.53-2.20 Å) crystal structures of the YSA peptide and several of its improved derivatives in complex with the EphA2 LBD, disclosing that YSA targets the ephrin-binding pocket of EphA2 and mimics binding features of the ephrin-A ligands. The structural information obtained enabled iterative peptide modifications conferring low nanomolar potency. Furthermore, contacts observed in the crystal structures shed light on how C-terminal features can convert YSA derivatives from antagonists to agonists that likely bivalently interact with two EphA2 molecules to promote receptor oligomerization, autophosphorylation, and downstream signaling. Consistent with this model, quantitative FRET measurements in live cells revealed that the peptide agonists promote the formation of EphA2 oligomeric assemblies. Our findings now enable rational strategies to differentially modify EphA2 signaling toward desired outcomes by using appropriately engineered peptides. Such peptides could be used as research tools to interrogate EphA2 function and to develop pharmacological leads.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Cancer Center, Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute, La Jolla, California 92037 and.