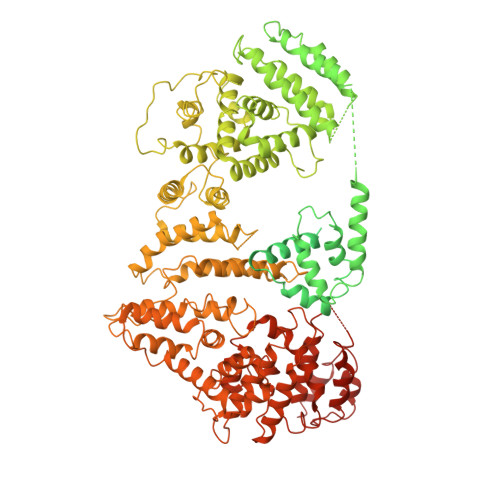
Structural basis of the fanconi anemia-associated mutations within the FANCA and FANCG complex.
Jeong, E., Lee, S.G., Kim, H.S., Yang, J., Shin, J., Kim, Y., Kim, J., Scharer, O.D., Kim, Y., Yeo, J.E., Kim, H.M., Cho, Y.(2020) Nucleic Acids Res 48: 3328-3342
- PubMed: 32002546
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa062
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LHS, 6LHU, 6LHV, 6LHW - PubMed Abstract:
Monoubiquitination of the Fanconi anemia complementation group D2 (FANCD2) protein by the FA core ubiquitin ligase complex is the central event in the FA pathway. FANCA and FANCG play major roles in the nuclear localization of the FA core complex. Mutations of these two genes are the most frequently observed genetic alterations in FA patients, and most point mutations in FANCA are clustered in the C-terminal domain (CTD). To understand the basis of the FA-associated FANCA mutations, we determined the cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of Xenopus laevis FANCA alone at 3.35 Å and 3.46 Å resolution and two distinct FANCA-FANCG complexes at 4.59 and 4.84 Å resolution, respectively. The FANCA CTD adopts an arc-shaped solenoid structure that forms a pseudo-symmetric dimer through its outer surface. FA- and cancer-associated point mutations are widely distributed over the CTD. The two different complex structures capture independent interactions of FANCG with either FANCA C-terminal HEAT repeats, or the N-terminal region. We show that mutations that disturb either of these two interactions prevent the nuclear localization of FANCA, thereby leading to an FA pathway defect. The structure provides insights into the function of FANCA CTD, and provides a framework for understanding FA- and cancer-associated mutations.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Life Science, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, 37673, Republic of Korea.