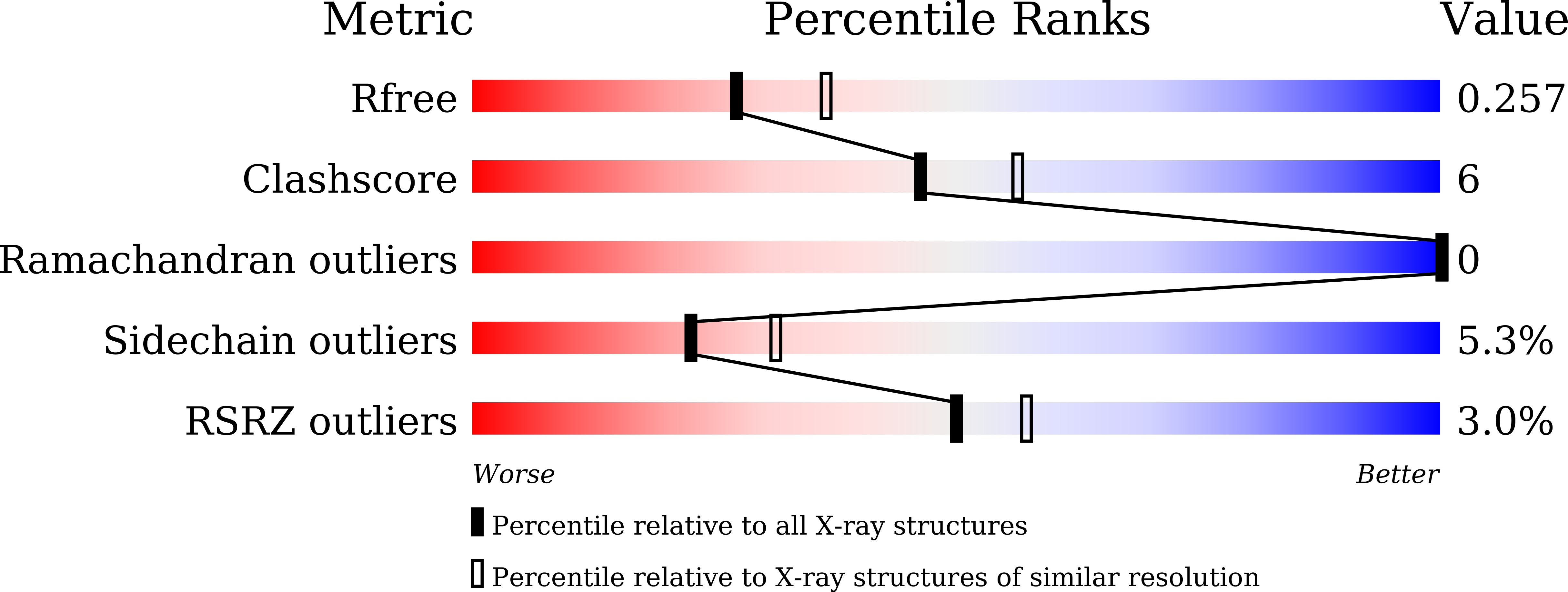
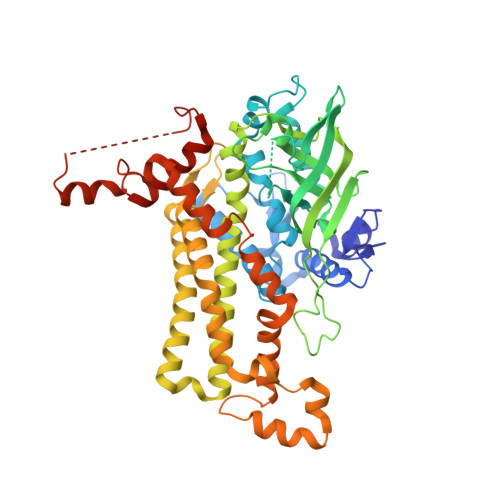
Identification of a Hotspot Residue for Improving the Thermostability of a Flavin-Dependent Monooxygenase.
Pongpamorn, P., Watthaisong, P., Pimviriyakul, P., Jaruwat, A., Lawan, N., Chitnumsub, P., Chaiyen, P.(2019) Chembiochem 20: 3020-3031
- PubMed: 31231908
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201900413
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6JHM - PubMed Abstract:
HadA is a flavin-dependent monooxygenase that can catalyze the denitration and dehalogenation of a wide variety of toxicants such as pesticides. Although these enzymatic reactions are useful for bioremediation or biocatalysis, the application of HadA for these purposes is not yet possible because of its low thermostability. In this work we have engineered HadA to be more thermostable through the use of structural, in silico, and rational approaches. The X-ray structure of HadA was solved to obtain a reliable three-dimensional protein model for further prediction of thermostable variants. In silico analysis by using two bioinformatic tools-FireProt and Disulfide by Design-suggested 102 variants that we then further refined by applying rational criteria including the location of a particular residue and its nearby interactions, as well as other biophysical parameters to narrow down the list to six candidates. The G513Y variant was found to be an optimal engineered candidate because it has significantly improved stability relative to the wild-type enzyme and equivalent activity. G513Y has an activity half-life 72 (50 °C) and 160 times (45 °C) longer than that of the wild-type enzyme. Coupled together with thermostable reactions of reduced flavin and NADH-regenerating systems, the G513Y variant can be used to catalyze denitration of 4nitrophenol at 45 °C. Structure/sequence alignments of HadA and its homologues indicate that several flavin-dependent monooxygenases also contain amino acid residues homologous to the G513 of HadA, hence opening up the possibility of applying this engineering approach to improving their thermostabilities as well. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations confirmed that the improved thermostability of the G513Y variant was due to aromatic hydrocarbon interactions between Y513 and N359, L347, G348, and F349.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biomolecular Science and Engineering, Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology (VISTEC), Wangchan Valley, Rayong, 21210, Thailand.