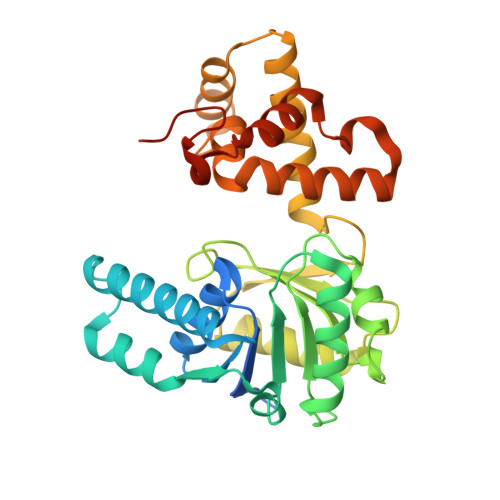
Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis FadB2 implicated in mycobacterial beta-oxidation.
Cox, J.A.G., Taylor, R.C., Brown, A.K., Attoe, S., Besra, G.S., Futterer, K.(2019) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 75: 101-108
- PubMed: 30644849
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798318017242
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HRD - PubMed Abstract:
The intracellular pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the causative agent of tuberculosis, which is a leading cause of mortality worldwide. The survival of M. tuberculosis in host macrophages through long-lasting periods of persistence depends, in part, on breaking down host cell lipids as a carbon source. The critical role of fatty-acid catabolism in this organism is underscored by the extensive redundancy of the genes implicated in β-oxidation (∼100 genes). In a previous study, the enzymology of the M. tuberculosis L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase FadB2 was characterized. Here, the crystal structure of this enzyme in a ligand-free form is reported at 2.1 Å resolution. FadB2 crystallized as a dimer with three unique dimer copies per asymmetric unit. The structure of the monomer reveals a dual Rossmann-fold motif in the N-terminal domain, while the helical C-terminal domain mediates dimer formation. Comparison with the CoA- and NAD + -bound human orthologue mitochondrial hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase shows extensive conservation of the residues that mediate substrate and cofactor binding. Superposition with the multi-catalytic homologue M. tuberculosis FadB, which forms a trifunctional complex with the thiolase FadA, indicates that FadB has developed structural features that prevent its self-association as a dimer. Conversely, FadB2 is unable to substitute for FadB in the tetrameric FadA-FadB complex as it lacks the N-terminal hydratase domain of FadB. Instead, FadB2 may functionally (or physically) associate with the enoyl-CoA hydratase EchA8 and the thiolases FadA2, FadA3, FadA4 or FadA6 as suggested by interrogation of the STRING protein-network database.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biosciences, University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham B15 2TT, England.