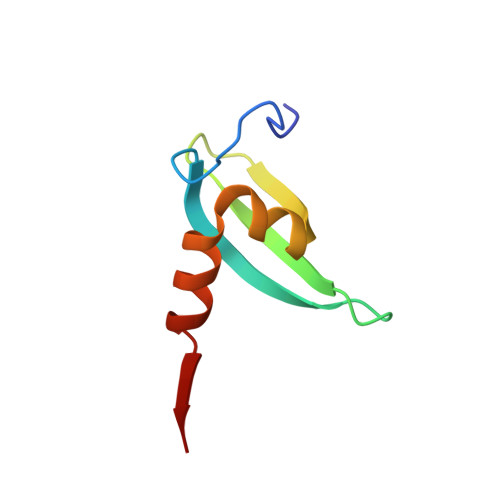
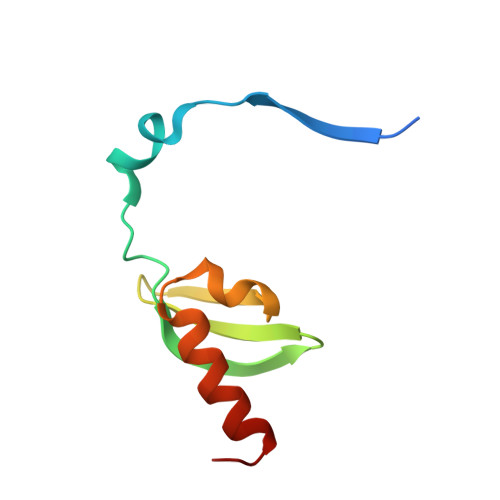
Transcriptional gene silencing requires dedicated interaction between HP1 protein Chp2 and chromatin remodeler Mit1.
Leopold, K., Stirpe, A., Schalch, T.(2019) Genes Dev 33: 565-577
- PubMed: 30808655
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.320440.118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6FTO - PubMed Abstract:
Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) proteins are key factors of eukaryotic heterochromatin that coordinate chromatin compaction and transcriptional gene silencing. Through their multivalency they act as adaptors between histone H3 Lys9 di/trimethyl marks in chromatin and effector complexes that bind to the HP1 chromoshadow domain. Most organisms encode for multiple HP1 isoforms and the molecular mechanisms that underpin their diverse functions in genome regulation remain poorly understood. In fission yeast, the two HP1 proteins Chp2 and Swi6 assume distinct roles and Chp2 is tightly associated with the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylation complex SHREC. Here we show that Chp2 directly engages the SHREC nucleosome remodeler subunit Mit1. The crystal structure of the interaction interface reveals an extraordinarily extensive and specific interaction between the chromoshadow domain of Chp2 and the N terminus of Mit1. The integrity of this interface is critical for high affinity binding and for heterochromatin formation. Comparison with Swi6 shows that the Chp2-Mit1 interface is highly selective and thereby provides the molecular basis for the functional specialization of an HP1 isoform.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, Faculty of Science, Sciences III, University of Geneva, CH-1211 Geneva 4, Switzerland.