Discovery and characterization of a thermostable two-domain GH6 endoglucanase from a compost metagenome.
Jensen, M.S., Fredriksen, L., MacKenzie, A.K., Pope, P.B., Leiros, I., Chylenski, P., Williamson, A.K., Christopeit, T., Ostby, H., Vaaje-Kolstad, G., Eijsink, V.G.H.(2018) PLoS One 13: e0197862-e0197862
- PubMed: 29795644
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197862
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6FAO - PubMed Abstract:
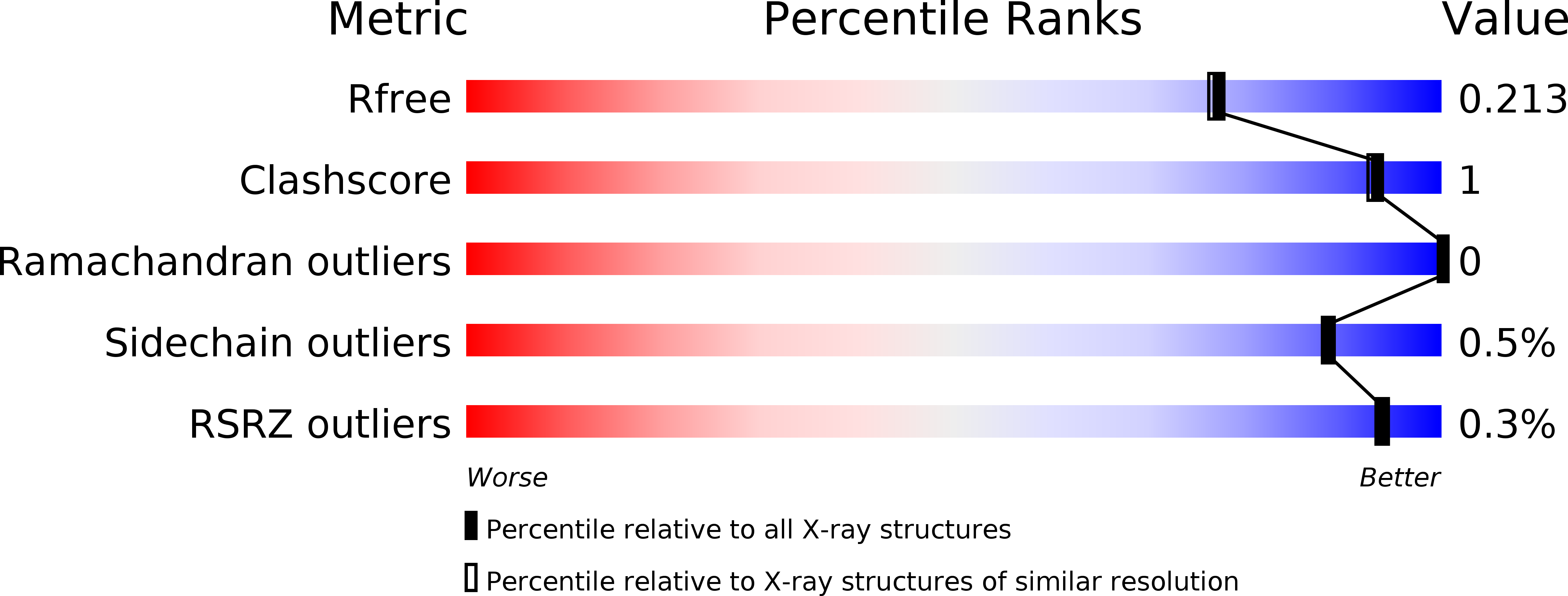
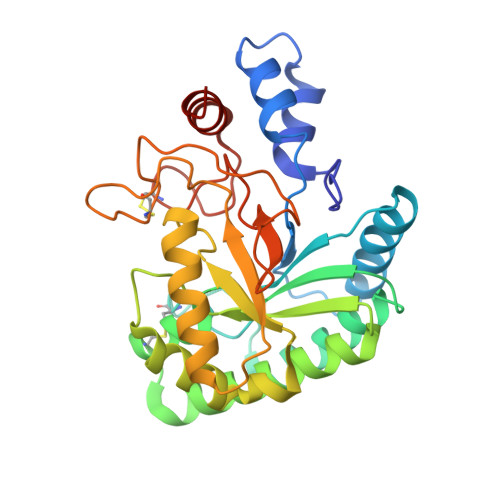
Enzymatic depolymerization of recalcitrant polysaccharides plays a key role in accessing the renewable energy stored within lignocellulosic biomass, and natural biodiversities may be explored to discover microbial enzymes that have evolved to conquer this task in various environments. Here, a metagenome from a thermophilic microbial community was mined to yield a novel, thermostable cellulase, named mgCel6A, with activity on an industrial cellulosic substrate (sulfite-pulped Norway spruce) and a glucomannanase side activity. The enzyme consists of a glycoside hydrolase family 6 catalytic domain (GH6) and a family 2 carbohydrate binding module (CBM2) that are connected by a linker rich in prolines and threonines. MgCel6A exhibited maximum activity at 85°C and pH 5.0 on carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), but in prolonged incubations with the industrial substrate, the highest yields were obtained at 60°C, pH 6.0. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) indicated a Tm(app) of 76°C. Both functional data and the crystal structure, solved at 1.88 Å resolution, indicate that mgCel6A is an endoglucanase. Comparative studies with a truncated variant of the enzyme showed that the CBM increases substrate binding, while not affecting thermal stability. Importantly, at higher substrate concentrations the full-length enzyme was outperformed by the catalytic domain alone, underpinning previous suggestions that CBMs may be less useful in high-consistency bioprocessing.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Chemistry, Biotechnology and Food Science, Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Ås, Norway.