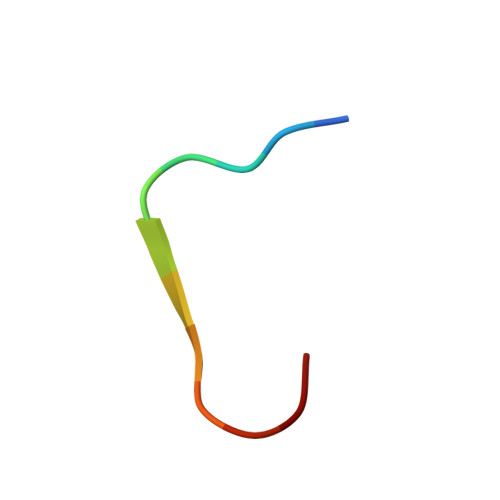
The BRD3 ET domain recognizes a short peptide motif through a mechanism that is conserved across chromatin remodelers and transcriptional regulators.
Wai, D.C.C., Szyszka, T.N., Campbell, A.E., Kwong, C., Wilkinson-White, L.E., Silva, A.P.G., Low, J.K.K., Kwan, A.H., Gamsjaeger, R., Chalmers, J.D., Patrick, W.M., Lu, B., Vakoc, C.R., Blobel, G.A., Mackay, J.P.(2018) J Biol Chem 293: 7160-7175
- PubMed: 29567837
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.000678
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BGG, 6BGH - PubMed Abstract:
Members of the bromodomain and extra-terminal domain (BET) family of proteins (bromodomain-containing (BRD) 2, 3, 4, and T) are widely expressed and highly conserved regulators of gene expression in eukaryotes. These proteins have been intimately linked to human disease, and more than a dozen clinical trials are currently underway to test BET-protein inhibitors as modulators of cancer. However, although it is clear that these proteins use their bromodomains to bind both histones and transcription factors bearing acetylated lysine residues, the molecular mechanisms by which BET family proteins regulate gene expression are not well defined. In particular, the functions of the other domains such as the ET domain have been less extensively studied. Here, we examine the properties of the ET domain of BRD3 as a protein/protein interaction module. Using a combination of pulldown and biophysical assays, we demonstrate that BRD3 binds to a range of chromatin-remodeling complexes, including the NuRD, BAF, and INO80 complexes, via a short linear "KIKL" motif in one of the complex subunits. NMR-based structural analysis revealed that, surprisingly, this mode of interaction is shared by the AF9 and ENL transcriptional coregulators that contain an acetyl-lysine-binding YEATS domain and regulate transcriptional elongation. This observation establishes a functional commonality between these two families of cancer-related transcriptional regulators. In summary, our data provide insight into the mechanisms by which BET family proteins might link chromatin acetylation to transcriptional outcomes and uncover an unexpected functional similarity between BET and YEATS family proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Sydney New South Wales 2006, Australia.