Mechanism of phosphoribosyl-ubiquitination mediated by a single Legionella effector.
Akturk, A., Wasilko, D.J., Wu, X., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Qiu, J., Luo, Z.Q., Reiter, K.H., Brzovic, P.S., Klevit, R.E., Mao, Y.(2018) Nature 557: 729-733
- PubMed: 29795346
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0147-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
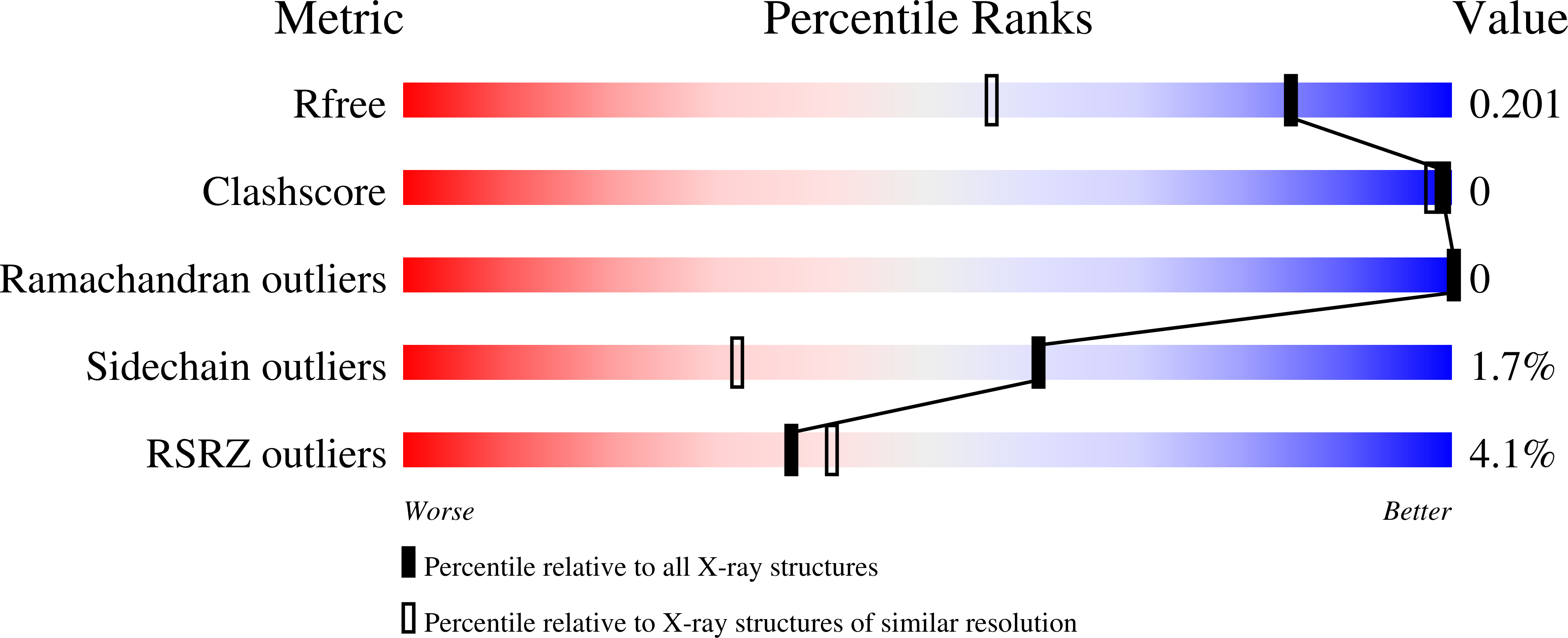
6B7M, 6B7O, 6B7P, 6B7Q - PubMed Abstract:
Ubiquitination is a post-translational modification that regulates many cellular processes in eukaryotes 1-4 . The conventional ubiquitination cascade culminates in a covalent linkage between the C terminus of ubiquitin (Ub) and a target protein, usually on a lysine side chain 1,5 . Recent studies of the Legionella pneumophila SidE family of effector proteins revealed a ubiquitination method in which a phosphoribosyl ubiquitin (PR-Ub) is conjugated to a serine residue on substrates via a phosphodiester bond 6-8 . Here we present the crystal structure of a fragment of the SidE family member SdeA that retains ubiquitination activity, and determine the mechanism of this unique post-translational modification. The structure reveals that the catalytic module contains two distinct functional units: a phosphodiesterase domain and a mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase domain. Biochemical analysis shows that the mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase domain-mediated conversion of Ub to ADP-ribosylated Ub (ADPR-Ub) and the phosphodiesterase domain-mediated ligation of PR-Ub to substrates are two independent activities of SdeA. Furthermore, we present two crystal structures of a homologous phosphodiesterase domain from the SidE family member SdeD 9 in complexes with Ub and ADPR-Ub. The structures suggest a mechanism for how SdeA processes ADPR-Ub to PR-Ub and AMP, and conjugates PR-Ub to a serine residue in substrates. Our study establishes the molecular mechanism of phosphoribosyl-linked ubiquitination and will enable future studies of this unusual type of ubiquitination in eukaryotes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Weill Institute for Cell and Molecular Biology and Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA.