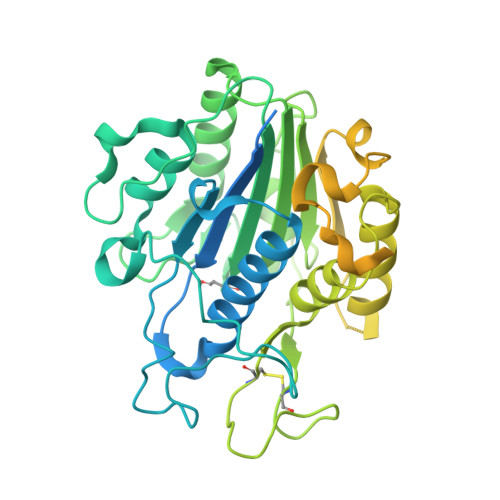
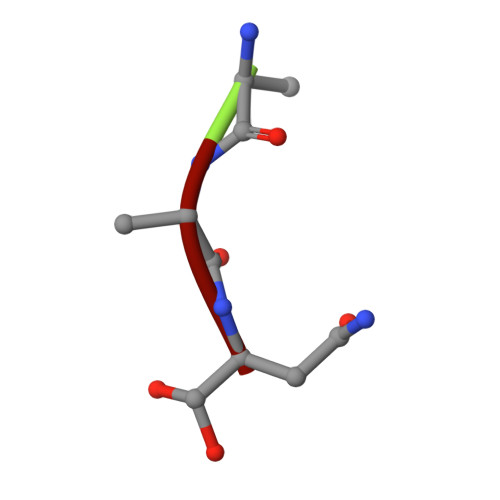
Structural basis of ribosomal peptide macrocyclization in plants.
Haywood, J., Schmidberger, J.W., James, A.M., Nonis, S.G., Sukhoverkov, K.V., Elias, M., Bond, C.S., Mylne, J.S.(2018) Elife 7
- PubMed: 29384475
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32955
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6AZT - PubMed Abstract:
Constrained, cyclic peptides encoded by plant genes represent a new generation of drug leads. Evolution has repeatedly recruited the Cys-protease asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP) to perform their head-to-tail ligation. These macrocyclization reactions use the substrates amino terminus instead of water to deacylate, so a peptide bond is formed. How solvent-exposed plant AEPs macrocyclize is poorly understood. Here we present the crystal structure of an active plant AEP from the common sunflower, Helianthus annuus . The active site contained electron density for a tetrahedral intermediate with partial occupancy that predicted a binding mode for peptide macrocyclization. By substituting catalytic residues we could alter the ratio of cyclic to acyclic products. Moreover, we showed AEPs from other species lacking cyclic peptides can perform macrocyclization under favorable pH conditions. This structural characterization of AEP presents a logical framework for engineering superior enzymes that generate macrocyclic peptide drug leads.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Molecular Sciences, The University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia.