Structural Basis for the Broad, Antibody-Mediated Neutralization of H5N1 Influenza Virus.
Lin, Q., Li, T., Chen, Y., Lau, S.Y., Wei, M., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., Yao, Q., Li, J., Li, Z., Wang, D., Zheng, Q., Yu, H., Gu, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, H., Li, S., Xia, N.(2018) J Virol 92
- PubMed: 29925655
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00547-18
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
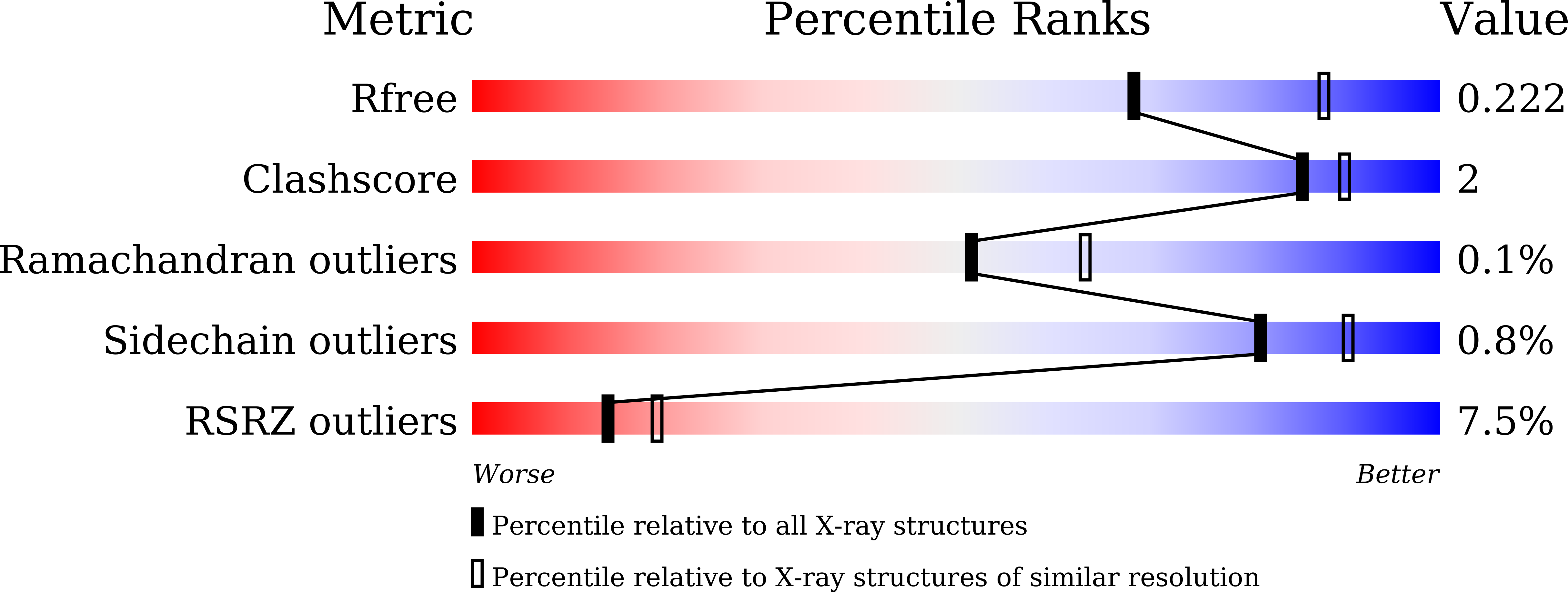
6A0X, 6A0Z - PubMed Abstract:
Human infection with highly pathogenic avian influenza A viruses causes severe disease and fatalities. We previously identified a potent and broadly neutralizing antibody (bnAb), 13D4, against the H5N1 virus. Here, we report the co-crystal structure of 13D4 in complex with the hemagglutinin (HA) of A/Vietnam/1194/2004 (H5N1). We show that heavy-chain complementarity-determining region 3 (HCDR3) of 13D4 confers broad yet specific neutralization against H5N1, undergoing conformational rearrangement to bind to the receptor binding site (RBS). Further, we show that mutating four critical residues within the RBS-Trp153, Lys156, Lys193, and Leu194-disrupts the binding between 13D4 and HA. Viruses bearing Asn193 instead of Lys/Arg can evade 13D4 neutralization, indicating that Lys193 polymorphism might be, at least in part, involved in the antigenicity of recent H5 genotypes (such as H5N6 and H5N8) as distinguished from H5N1. BnAb 13D4 may offers a template for therapeutic RBS inhibitor design and serve as an indicator of antigenic change for current H5 viruses. IMPORTANCE Infection by highly pathogenic avian influenza A virus remains a threat to public health. Our broadly neutralizing antibody, 13D4, is capable of neutralizing all representative H5N1 viruses and protecting mice against lethal challenge. Structural analysis revealed that 13D4 uses heavy-chain complementarity-determining region 3 (HCDR3) to fit the receptor binding site (RBS) via conformational rearrangement. Four conserved residues within the RBS are critical for the broad potency of 13D4. Importantly, polymorphism of Lys193 on the RBS may be associated with the antigenicity shift from H5N1 to other newly emerging viruses, such as H5N6 and H5N8. Our findings may pave the way for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus vaccine development and therapeutic RBS inhibitor design.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Vaccinology and Molecular Diagnostics, School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China.