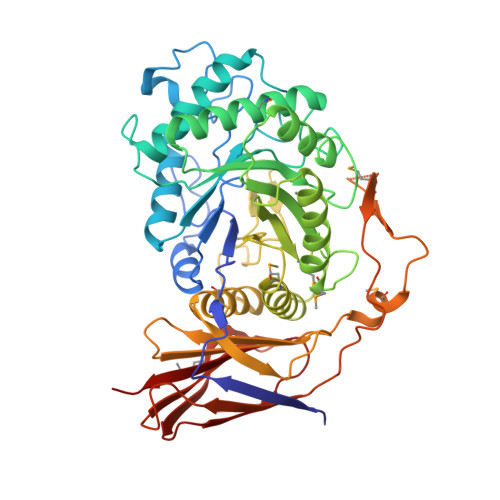
Structural and Functional Insights Into CmGH1, a Novel GH39 Family beta-Glucosidase From Deep-Sea Bacterium.
Shen, Y., Li, Z., Huo, Y.Y., Bao, L., Gao, B., Xiao, P., Hu, X., Xu, X.W., Li, J.(2019) Front Microbiol 10: 2922-2922
- PubMed: 31921083
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02922
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
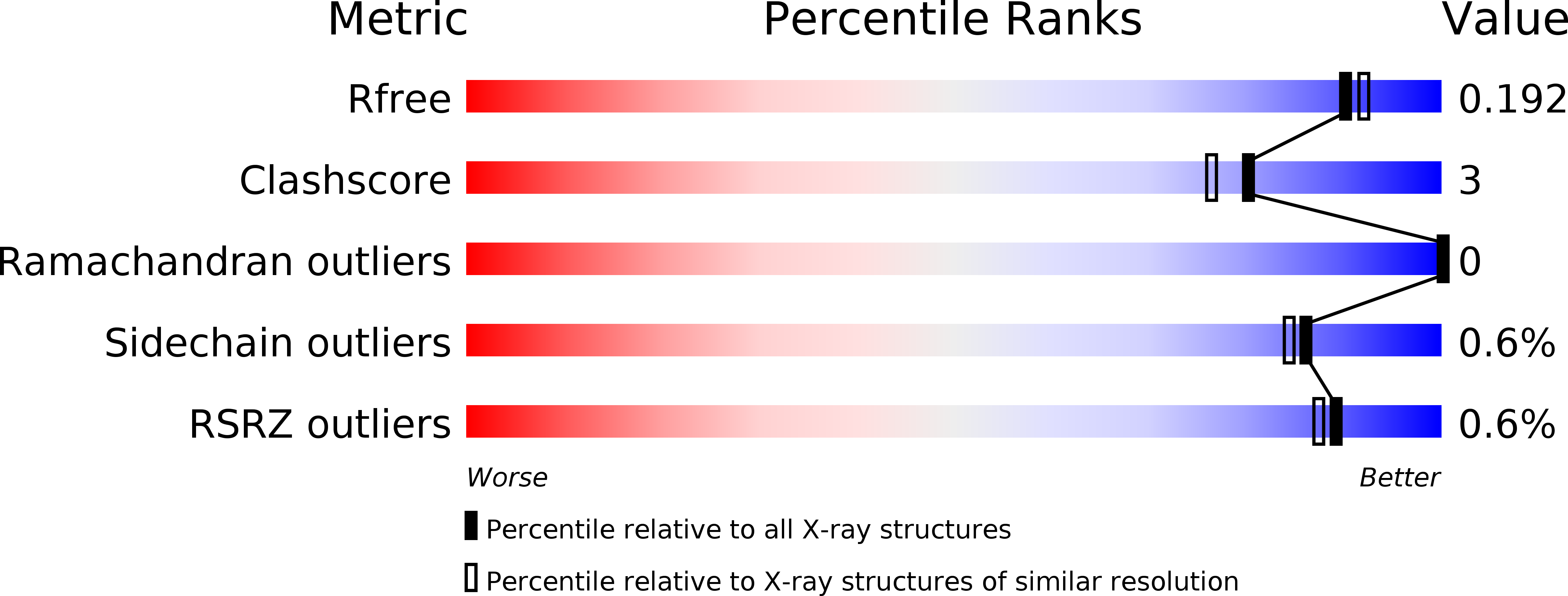
5Z3K - PubMed Abstract:
Glucosidases play key roles in many diseases and are limiting enzymes during cellulose degradation, which is an important part of global carbon cycle. Here, we identified a novel β-glucosidase, CmGH1, isolated from marine bacterium Croceicoccus marinus E4A9 T . In spite of its high sequence and structural similarity with β-xylosidase family members, CmGH1 had enzymatic activity toward p -nitrophenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside ( p- NPG) and cellobiose. The K m and K cat values of CmGH1 toward p- NPG were 0.332 ± 0.038 mM and 2.15 ± 0.081 min -1 , respectively. CmGH1 was tolerant to high concentration salts, detergents, as well as many kinds of organic solvents. The crystal structure of CmGH1 was resolved with a 1.8 Å resolution, which showed that CmGH1 was composed of a canonical (α/β) 8 -barrel catalytic domain and an auxiliary β-sandwich domain. Although no canonical catalytic triad residues were found in CmGH1, structural comparison and mutagenesis analysis suggested that residues Gln157 and Tyr264 of CmGH1 were the active sites. Mutant Q157E significantly increased its hydrolase activity up to 15-fold, whereas Y264E totally abolished its enzymatic activity. These results might provide new insights into understanding the different catalytic mechanism during evolution for β-glucosidases and β-xylosidases.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Department of Neurology, School of Life Sciences, Huashan Hospital, Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Industrial Microorganisms, Fudan University, Shanghai, China.