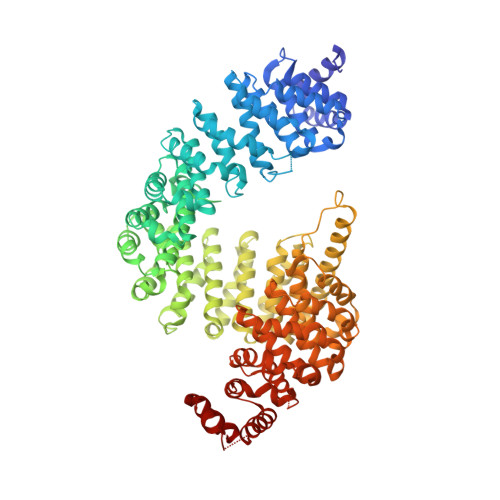
Nuclear Import Receptor Inhibits Phase Separation of FUS through Binding to Multiple Sites.
Yoshizawa, T., Ali, R., Jiou, J., Fung, H.Y.J., Burke, K.A., Kim, S.J., Lin, Y., Peeples, W.B., Saltzberg, D., Soniat, M., Baumhardt, J.M., Oldenbourg, R., Sali, A., Fawzi, N.L., Rosen, M.K., Chook, Y.M.(2018) Cell 173: 693-705.e22
- PubMed: 29677513
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YVG, 5YVH, 5YVI - PubMed Abstract:
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) is believed to underlie formation of biomolecular condensates, cellular compartments that concentrate macromolecules without surrounding membranes. Physical mechanisms that control condensate formation/dissolution are poorly understood. The RNA-binding protein fused in sarcoma (FUS) undergoes LLPS in vitro and associates with condensates in cells. We show that the importin karyopherin-β2/transportin-1 inhibits LLPS of FUS. This activity depends on tight binding of karyopherin-β2 to the C-terminal proline-tyrosine nuclear localization signal (PY-NLS) of FUS. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analyses reveal weak interactions of karyopherin-β2 with sequence elements and structural domains distributed throughout the entirety of FUS. Biochemical analyses demonstrate that most of these same regions also contribute to LLPS of FUS. The data lead to a model where high-affinity binding of karyopherin-β2 to the FUS PY-NLS tethers the proteins together, allowing multiple, distributed weak intermolecular contacts to disrupt FUS self-association, blocking LLPS. Karyopherin-β2 may act analogously to control condensates in diverse cellular contexts.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX 75390, USA.