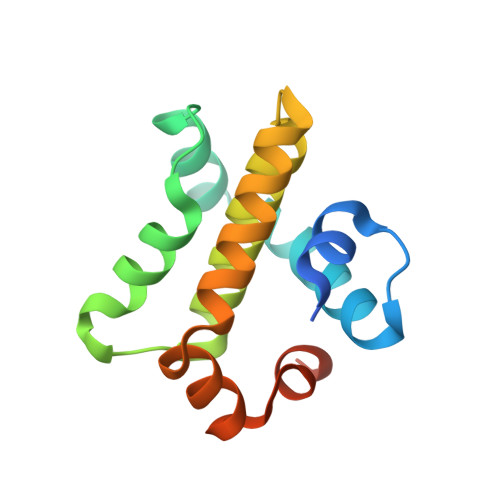
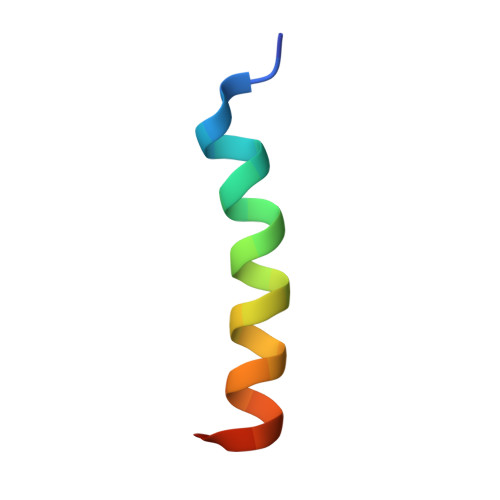
Grouper iridovirus GIV66 is a Bcl-2 protein that inhibits apoptosis by exclusively sequestering Bim.
Banjara, S., Mao, J., Ryan, T.M., Caria, S., Kvansakul, M.(2018) J Biol Chem 293: 5464-5477
- PubMed: 29483196
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.000591
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
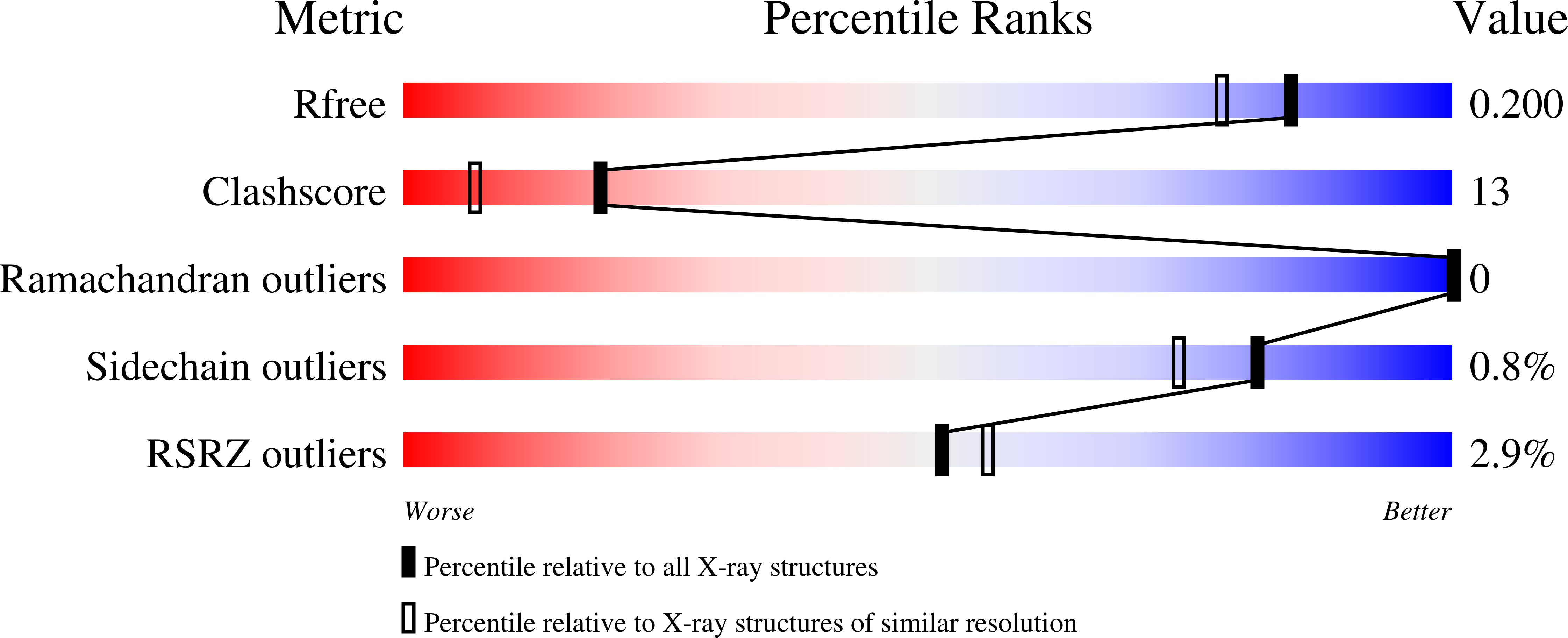
5VMN, 5VMO - PubMed Abstract:
Programmed cell death or apoptosis is a critical mechanism for the controlled removal of damaged or infected cells, and proteins of the Bcl-2 family are important arbiters of this process. Viruses have been shown to encode functional and structural homologs of Bcl-2 to counter premature host-cell apoptosis and ensure viral proliferation or survival. Grouper iridovirus (GIV) is a large DNA virus belonging to the Iridoviridae family and harbors GIV66, a putative Bcl-2-like protein and mitochondrially localized apoptosis inhibitor. However, the molecular and structural basis of GIV66-mediated apoptosis inhibition is currently not understood. To gain insight into GIV66's mechanism of action, we systematically evaluated its ability to bind peptides spanning the BH3 domain of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members. Our results revealed that GIV66 harbors an unusually high level of specificity for pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 and displays affinity only for Bcl-2-like 11 (Bcl2L11 or Bim). Using crystal structures of both apo-GIV66 and GIV66 bound to the BH3 domain from Bim, we unexpectedly found that GIV66 forms dimers via an interface that results in occluded access to the canonical Bcl-2 ligand-binding groove, which breaks apart upon Bim binding. This observation suggests that GIV66 dimerization may affect GIV66's ability to bind host pro-death Bcl-2 proteins and enables highly targeted virus-directed suppression of host apoptosis signaling. Our findings provide a mechanistic understanding for the potent anti-apoptotic activity of GIV66 by identifying it as the first single-specificity, pro-survival Bcl-2 protein and identifying a pivotal role of Bim in GIV-mediated inhibition of apoptosis.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Biochemistry and Genetics, La Trobe Institute for Molecular Science, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria 3086, Australia and.