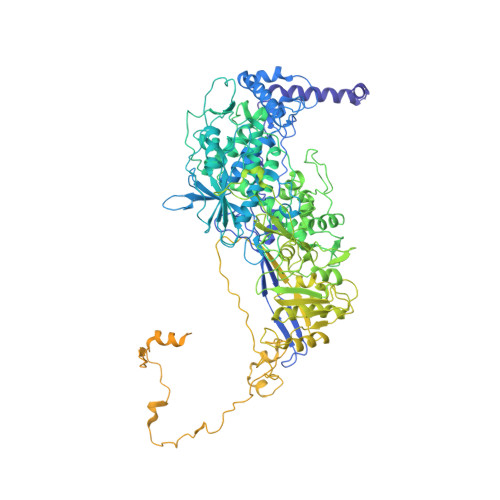
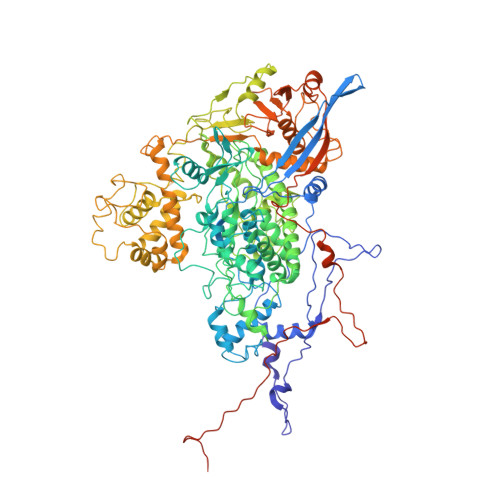
Acquisition of functions on the outer capsid surface during evolution of double-stranded RNA fungal viruses.
Mata, C.P., Luque, D., Gomez-Blanco, J., Rodriguez, J.M., Gonzalez, J.M., Suzuki, N., Ghabrial, S.A., Carrascosa, J.L., Trus, B.L., Caston, J.R.(2017) PLoS Pathog 13: e1006755-e1006755
- PubMed: 29220409
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006755
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5ND1 - PubMed Abstract:
Unlike their counterparts in bacterial and higher eukaryotic hosts, most fungal viruses are transmitted intracellularly and lack an extracellular phase. Here we determined the cryo-EM structure at 3.7 Å resolution of Rosellinia necatrix quadrivirus 1 (RnQV1), a fungal double-stranded (ds)RNA virus. RnQV1, the type species of the family Quadriviridae, has a multipartite genome consisting of four monocistronic segments. Whereas most dsRNA virus capsids are based on dimers of a single protein, the ~450-Å-diameter, T = 1 RnQV1 capsid is built of P2 and P4 protein heterodimers, each with more than 1000 residues. Despite a lack of sequence similarity between the two proteins, they have a similar α-helical domain, the structural signature shared with the lineage of the dsRNA bluetongue virus-like viruses. Domain insertions in P2 and P4 preferential sites provide additional functions at the capsid outer surface, probably related to enzyme activity. The P2 insertion has a fold similar to that of gelsolin and profilin, two actin-binding proteins with a function in cytoskeleton metabolism, whereas the P4 insertion suggests protease activity involved in cleavage of the P2 383-residue C-terminal region, absent in the mature viral particle. Our results indicate that the intimate virus-fungus partnership has altered the capsid genome-protective and/or receptor-binding functions. Fungal virus evolution has tended to allocate enzyme activities to the virus capsid outer surface.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structure of Macromolecules, Centro Nacional de Biotecnología (CNB-CSIC), Campus Cantoblanco, Madrid, Spain.