A family of archaea-like carboxylesterases preferentially expressed in the symbiotic phase of the mycorrhizal fungus Tuber melanosporum.
Cavazzini, D., Grossi, G., Levati, E., Vallese, F., Montanini, B., Bolchi, A., Zanotti, G., Ottonello, S.(2017) Sci Rep 7: 7628-7628
- PubMed: 28794466
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08007-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
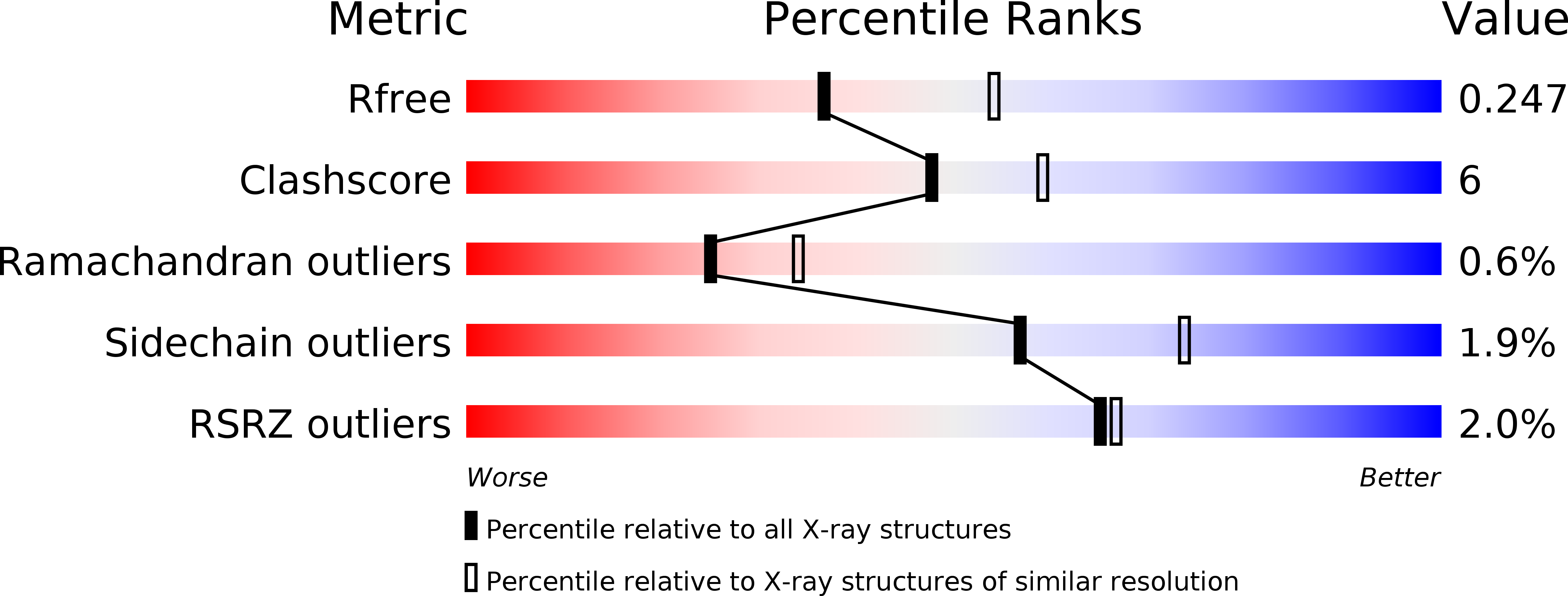
5MIF, 5MII - PubMed Abstract:
An increasing number of esterases is being revealed by (meta) genomic sequencing projects, but few of them are functionally/structurally characterized, especially enzymes of fungal origin. Starting from a three-member gene family of secreted putative "lipases/esterases" preferentially expressed in the symbiotic phase of the mycorrhizal fungus Tuber melanosporum ("black truffle"), we show here that these enzymes (TmelEST1-3) are dimeric, heat-resistant carboxylesterases capable of hydrolyzing various short/medium chain p-nitrophenyl esters. TmelEST2 was the most active (kcat = 2302 s -1 for p-nitrophenyl-butyrate) and thermally stable (T 50 = 68.3 °C), while TmelEST3 was the only one displaying some activity on tertiary alcohol esters. X-ray diffraction analysis of TmelEST2 revealed a classical α/β hydrolase-fold structure, with a network of dimer-stabilizing intermolecular interactions typical of archaea esterases. The predicted structures of TmelEST1 and 3 are overall quite similar to that of TmelEST2 but with some important differences. Most notably, the much smaller volume of the substrate-binding pocket and the more acidic electrostatic surface profile of TmelEST1. This was also the only TmelEST capable of hydrolyzing feruloyl-esters, suggestinng a possible role in root cell-wall deconstruction during symbiosis establishment. In addition to their potential biotechnological interest, TmelESTs raise important questions regarding the evolutionary recruitment of archaea-like enzymes into mesophilic subterranean fungi such as truffles.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemical Life Sciences and Environmental Sustainability, University of Parma, Parco Area delle Scienze 23/A, 43124, Parma, Italy.