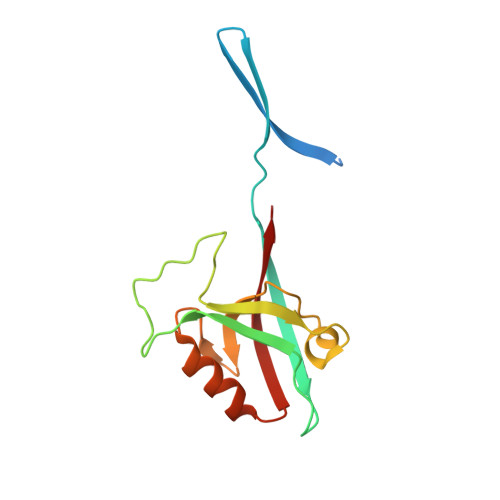
A binding site outside the canonical PDZ domain determines the specific interaction between Shank and SAPAP and their function
Zeng, M., Shang, Y., Guo, T., He, Q., Yung, W.H., Liu, K., Zhang, M.(2016) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113: E3081-E3090
- PubMed: 27185935
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1523265113
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5IZU - PubMed Abstract:
Shank and SAPAP (synapse-associated protein 90/postsynaptic density-95-associated protein) are two highly abundant scaffold proteins that directly interact with each other to regulate excitatory synapse development and plasticity. Mutations of SAPAP, but not other reported Shank PDZ domain binders, share a significant overlap on behavioral abnormalities with the mutations of Shank both in patients and in animal models. The molecular mechanism governing the exquisite specificity of the Shank/SAPAP interaction is not clear, however. Here we report that a sequence preceding the canonical PDZ domain of Shank, together with the elongated PDZ BC loop, form another binding site for a sequence upstream of the SAPAP PDZ-binding motif, leading to a several hundred-fold increase in the affinity of the Shank/SAPAP interaction. We provide evidence that the specific interaction afforded by this newly identified site is required for Shank synaptic targeting and the Shank-induced synaptic activity increase. Our study provides a molecular explanation of how Shank and SAPAP dosage changes due to their gene copy number variations can contribute to different psychiatric disorders.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Life Science, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China;