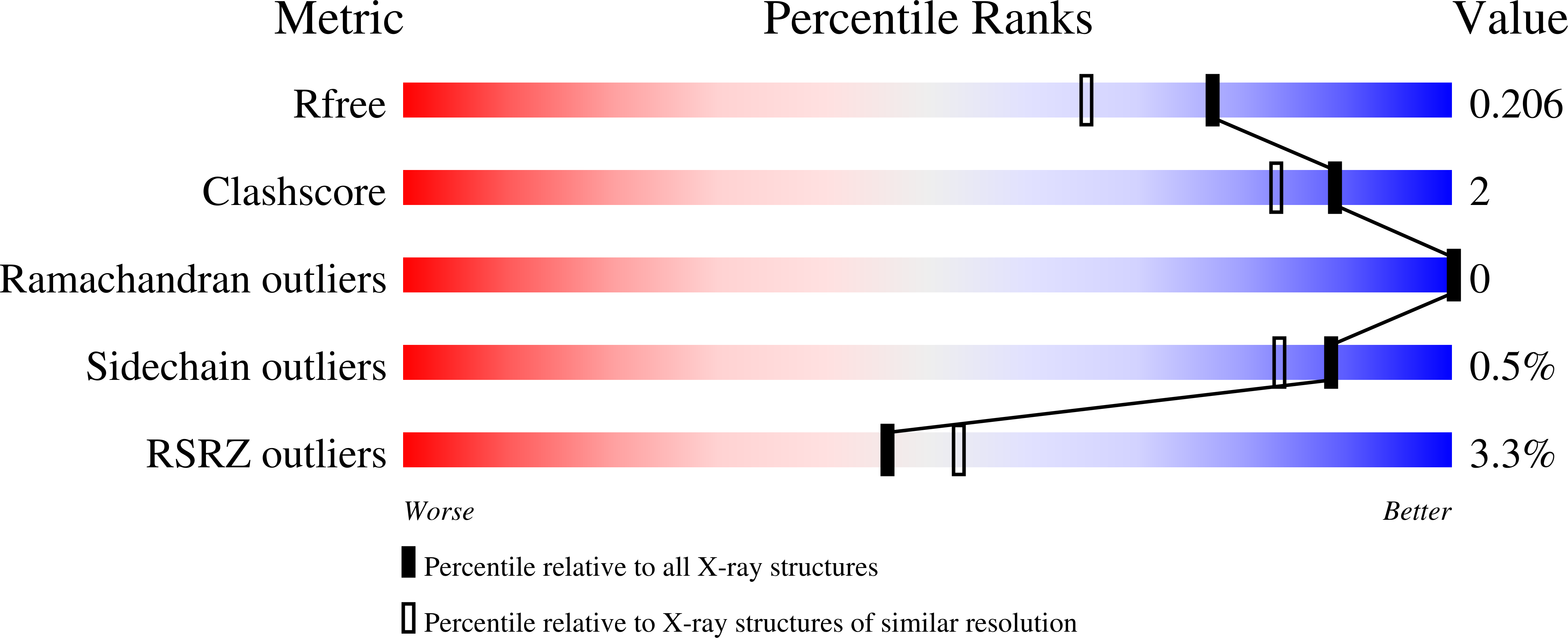
Exploring the structure of glutamate racemase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis as a template for anti-mycobacterial drug discovery.
Poen, S., Nakatani, Y., Opel-Reading, H.K., Lasse, M., Dobson, R.C., Krause, K.L.(2016) Biochem J 473: 1267-1280
- PubMed: 26964898
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160186
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5HJ7, 5IJW - PubMed Abstract:
Glutamate racemase (MurI) is responsible for providing D-glutamate for peptidoglycan biosynthesis in bacteria and has been a favoured target in pharmaceutical drug design efforts. It has recently been proven to be essential in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative organism of tuberculosis, a disease for which new medications are urgently needed. In the present study, we have determined the protein crystal structures of MurI from both M. tuberculosis and Mycobacterium smegmatis in complex with D-glutamate to 2.3 Å and 1.8 Å resolution respectively. These structures are conserved, but reveal differences in their active site architecture compared with that of other MurI structures. Furthermore, compounds designed to target other glutamate racemases have been screened but do not inhibit mycobacterial MurI, suggesting that a new drug design effort will be needed to develop inhibitors. A new type of MurI dimer arrangement has been observed in both structures, and this arrangement becomes the third biological dimer geometry for MurI found to date. The mycobacterial MurI dimer is tightly associated, with a KD in the nanomolar range. The enzyme binds D- and L-glutamate specifically, but is inactive in solution unless the dimer interface is mutated. We created triple mutants of this interface in the M. smegmatis glutamate racemase (D26R/R105A/G194R or E) that have appreciable activity (kcat=0.056-0.160 min(-1) and KM=0.26-0.51 mM) and can be utilized to screen proposed antimicrobial candidates for inhibition.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Otago, PO Box 56, Dunedin 9054, New Zealand.