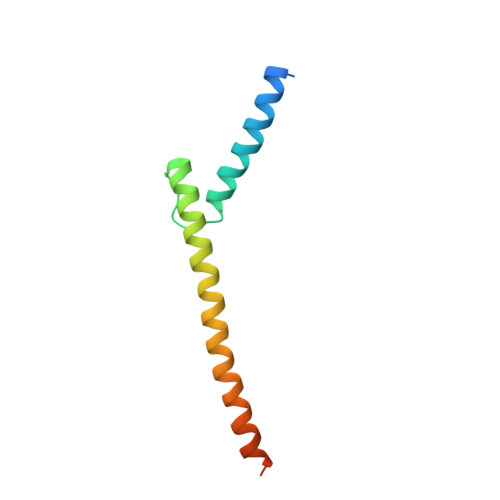
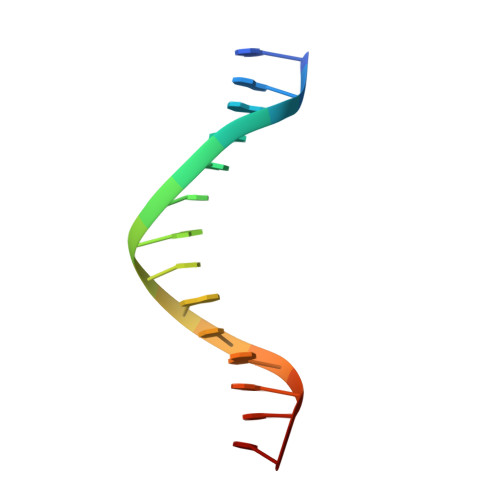
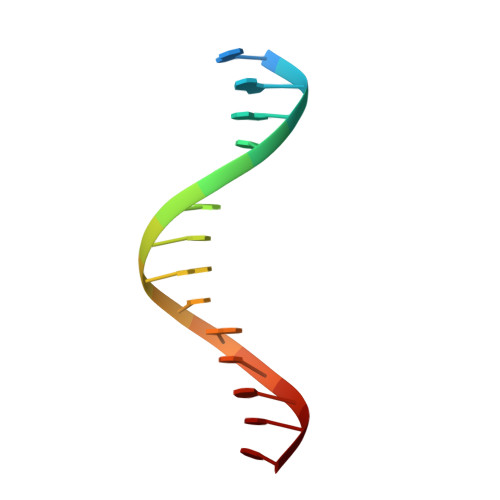
Crystal Structure of Tetrameric Arabidopsis MYC2 Reveals the Mechanism of Enhanced Interaction with DNA.
Lian, T.F., Xu, Y.P., Li, L.F., Su, X.D.(2017) Cell Rep 19: 1334-1342
- PubMed: 28514654
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.057
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5GNJ - PubMed Abstract:
Jasmonates (JAs) are essential plant hormones that play important roles in the regulation of plant growth and the response to environmental stress. In the JA signaling pathway, the core transcription factors are a class of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins, including MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4, that have different regulatory capacities. Here, we report the 2.7 Å crystal structure of the MYC2 bHLH domain complexed with G-box DNA, showing a cis-tetrameric structure. Biochemical assays confirmed that full-length MYC2 forms a stable homo-tetramer both in solution and in DNA-bound states, whereas MYC3 forms only a homodimer. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) assays demonstrated that tetramerization enhanced DNA binding affinity, and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assay indicated DNA looping potential of tetrameric MYC2. Luciferase assay further confirmed the importance of tetramerization in transcriptional regulation. Our studies provide a mechanistic explanation for the regulatory differences of MYC transcription factors.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Protein and Plant Gene Research and Biodynamic Optical Imaging Center (BIOPIC), School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China.