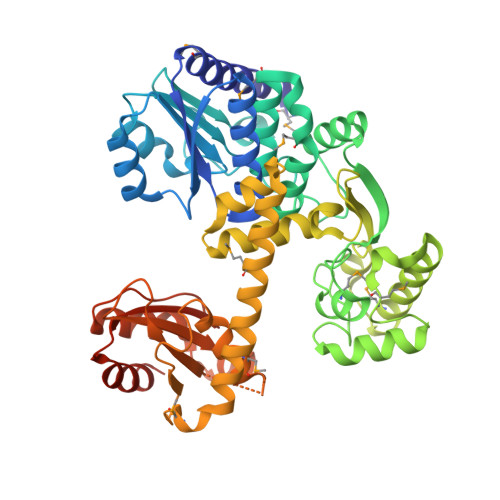
Atomic structure of an archaeal GAN suggests its dual roles as an exonuclease in DNA repair and a CMG component in DNA replication.
Oyama, T., Ishino, S., Shirai, T., Yamagami, T., Nagata, M., Ogino, H., Kusunoki, M., Ishino, Y.(2016) Nucleic Acids Res 44: 9505-9517
- PubMed: 27599844
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw789
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5GHR, 5GHS, 5GHT - PubMed Abstract:
In eukaryotic DNA replication initiation, hexameric MCM (mini-chromosome maintenance) unwinds the template double-stranded DNA to form the replication fork. MCM is activated by two proteins, Cdc45 and GINS, which constitute the 'CMG' unwindosome complex together with the MCM core. The archaeal DNA replication system is quite similar to that of eukaryotes, but only limited knowledge about the DNA unwinding mechanism is available, from a structural point of view. Here, we describe the crystal structure of an archaeal GAN (GINS-associated nuclease) from Thermococcus kodakaraensis, the homolog of eukaryotic Cdc45, in both the free form and the complex with the C-terminal domain of the cognate Gins51 subunit (Gins51C). This first archaeal GAN structure exhibits a unique, 'hybrid' structure between the bacterial RecJ and the eukaryotic Cdc45. GAN possesses the conserved DHH and DHH1 domains responsible for the exonuclease activity, and an inserted CID (CMG interacting domain)-like domain structurally comparable to that in Cdc45, suggesting its dual roles as an exonuclease in DNA repair and a CMG component in DNA replication. A structural comparison of the GAN-Gins51C complex with the GINS tetramer suggests that GINS uses the mobile Gins51C as a hook to bind GAN for CMG formation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Yamanashi, 4-4-37 Takeda, Kofu, Yamanashi 400-8510, Japan takujio@yamanashi.ac.jp.