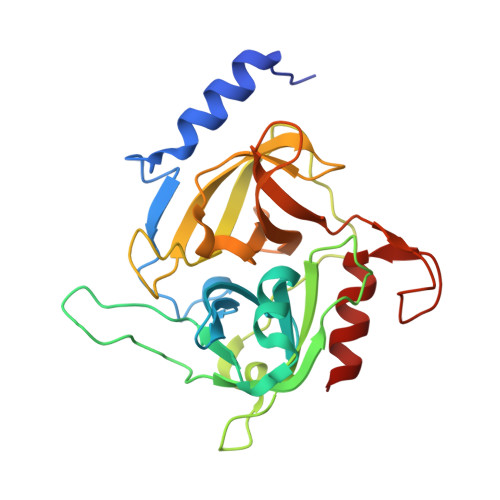
Crystal structure of Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxin D-like protein: Structural basis for the high specificity of exfoliative toxins.
Mariutti, R.B., Souza, T.A., Ullah, A., Caruso, I.P., de Moraes, F.R., Zanphorlin, L.M., Tartaglia, N.R., Seyffert, N., Azevedo, V.A., Le Loir, Y., Murakami, M.T., Arni, R.K.(2015) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 467: 171-177
- PubMed: 26299923
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.08.083
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5C2Z - PubMed Abstract:
Exfoliative toxins are serine proteases secreted by Staphylococcus aureus that are associated with toxin-mediated staphylococcal syndromes. To date, four different serotypes of exfoliative toxins have been identified and 3 of them (ETA, ETB, and ETD) are linked to human infection. Among these toxins, only the ETD structure remained unknown, limiting our understanding of the structural determinants for the functional differentiation between these toxins. We recently identified an ETD-like protein associated to S. aureus strains involved in mild mastitis in sheep. The crystal structure of this ETD-like protein was determined at 1.95 Å resolution and the structural analysis provide insights into the oligomerization, stability and specificity and enabled a comprehensive structural comparison with ETA and ETB. Despite the highly conserved molecular architecture, significant differences in the composition of the loops and in both the N- and C-terminal α-helices seem to define ETD-like specificity. Molecular dynamics simulations indicate that these regions defining ET specificity present different degrees of flexibility and may undergo conformational changes upon substrate recognition and binding. DLS and AUC experiments indicated that the ETD-like is monomeric in solution whereas it is present as a dimer in the asymmetric unit indicating that oligomerization is not related to functional differentiation among these toxins. Differential scanning calorimetry and circular dichroism assays demonstrated an endothermic transition centered at 52 °C, and an exothermic aggregation in temperatures up to 64 °C. All these together provide insights about the mode of action of a toxin often secreted in syndromes that are not associated with either ETA or ETB.
Organizational Affiliation:
Multi User Center for Biomolecular Innovation, Department of Physics, IBILCE/UNESP, São José do Rio Preto, SP, Brazil.