Structure, mechanism, and phylogeny of LysM-chitinase conjugates specifically found in fern plants.
Kitaoku, Y., Taira, T., Numata, T., Ohnuma, T., Fukamizo, T.(2022) Plant Sci 321: 111310-111310
- PubMed: 35696910
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2022.111310
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5BUM - PubMed Abstract:
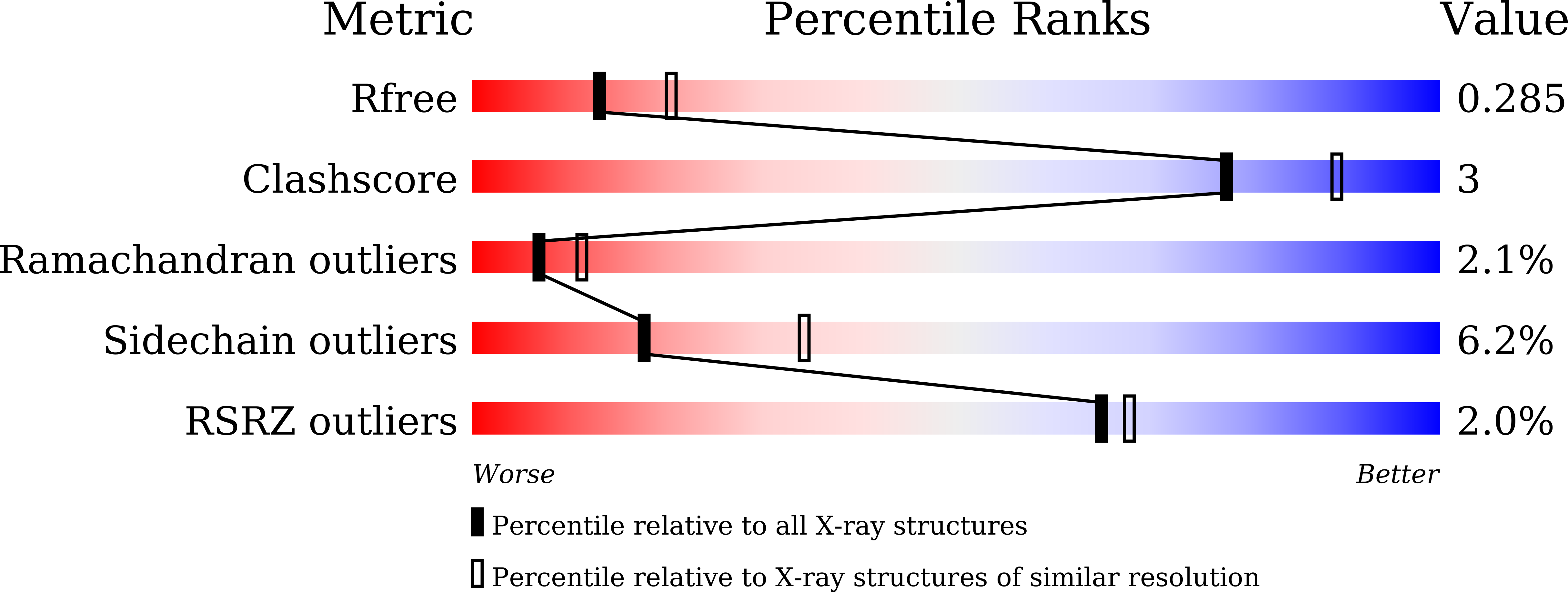
A unique GH18 chitinase containing two N-terminal lysin motifs (PrLysM1 and PrLysM2) was first found in fern, Pteris ryukyuensis (Onaga and Taira, Glycobiology, 18, 414-423, 2008). This type of LysM-chitinase conjugates is not usually found in plants but in fungi. Here, we produced a similar GH18 chitinase with one N-terminal LysM module (EaLysM) from the fern, Equisetum arvense (EaChiA, Inamine et al., Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 79, 1296-1304, 2015), using an Escherichia coli expression system and characterized for its structure and mechanism of action. The crystal structure of EaLysM exhibited an almost identical fold (βααβ) to that of PrLysM2. From isothermal titration calorimetry and nuclear magnetic resonance, the binding mode and affinities of EaLysM for chitooligosaccharides (GlcNAc) n (3, 4, 5, and 6) were found to be comparable to those of PrLysM2. The LysM module in EaChiA is likely to bind (GlcNAc) n almost independently through CH-π stacking of a Tyr residue with the pyranose ring. The (GlcNAc) n -binding mode of LysMs in the LysM-chitinase conjugates from fern plants appears to differ from that of plant LysMs acting in chitin- or Nod-signal perception, in which multiple LysMs cooperatively act on (GlcNAc) n . Phylogenetic analysis suggested that LysM-GH18 conjugates of fern plants formed a monophyletic group and had been separated earlier than forming the clade of fungal chitinases with LysMs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Advanced Bioscience, Kindai University, 3327-204, Nakamachi, Nara 631-8505, Japan.