Carbon Dioxide "Trapped" in a beta-Carbonic Anhydrase.
Aggarwal, M., Chua, T.K., Pinard, M.A., Szebenyi, D.M., McKenna, R.(2015) Biochemistry 54: 6631-6638
- PubMed: 26457866
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00987
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
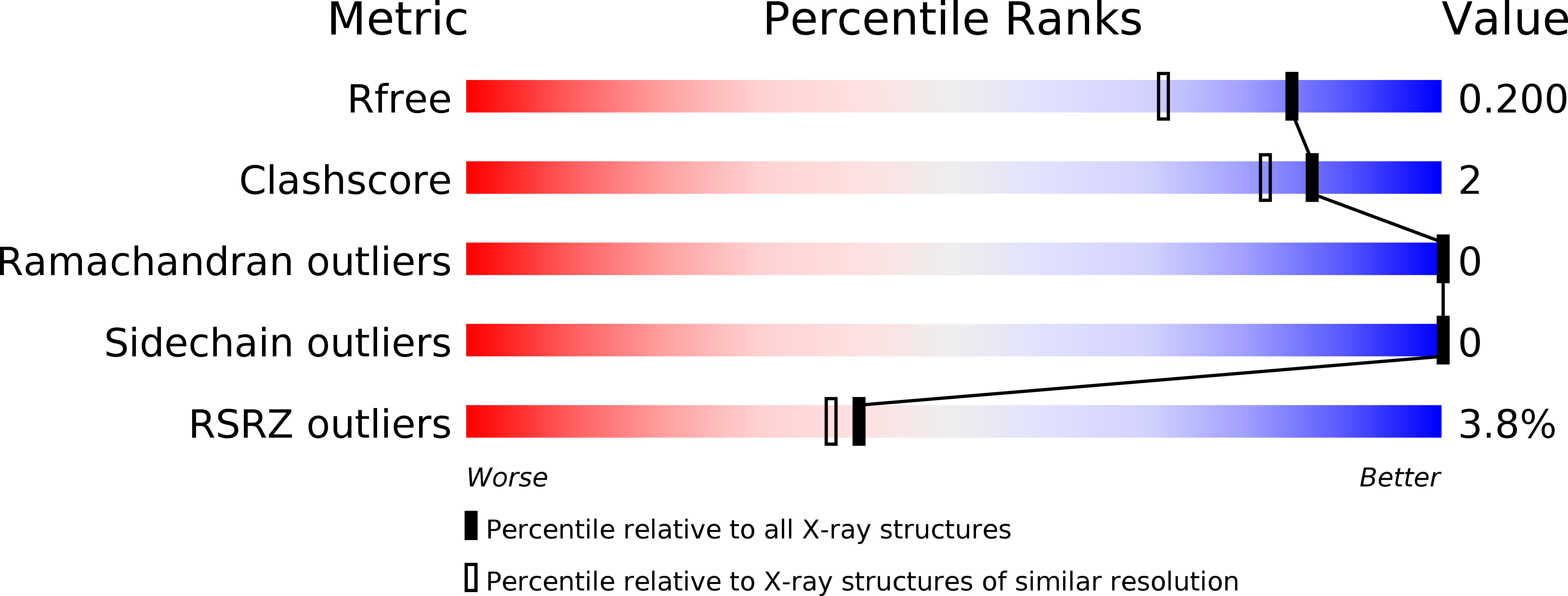
5BQ1 - PubMed Abstract:
Carbonic anhydrases (CAs) are enzymes that catalyze the hydration/dehydration of CO2/HCO3(-) with rates approaching diffusion-controlled limits (kcat/KM ∼ 10(8) M(-1) s(-1)). This family of enzymes has evolved disparate protein folds that all perform the same reaction at near catalytic perfection. Presented here is a structural study of a β-CA (psCA3) expressed in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, in complex with CO2, using pressurized cryo-cooled crystallography. The structure has been refined to 1.6 Å resolution with R(cryst) and R(free) values of 17.3 and 19.9%, respectively, and is compared with the α-CA, human CA isoform II (hCA II), the only other CA to have CO2 captured in its active site. Despite the lack of structural similarity between psCA3 and hCA II, the CO2 binding orientation relative to the zinc-bound solvent is identical. In addition, a second CO2 binding site was located at the dimer interface of psCA3. Interestingly, all β-CAs function as dimers or higher-order oligomeric states, and the CO2 bound at the interface may contribute to the allosteric nature of this family of enzymes or may be a convenient alternative binding site as this pocket has been previously shown to be a promiscuous site for a variety of ligands, including bicarbonate, sulfate, and phosphate ions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biology and Soft Matter, Oak Ridge National Laboratory , Oak Ridge, Tennessee 37831, United States.