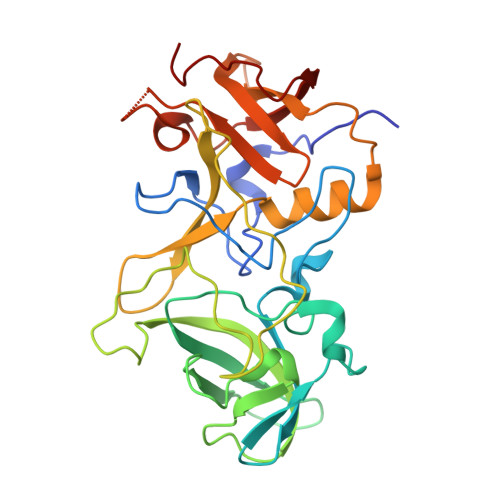
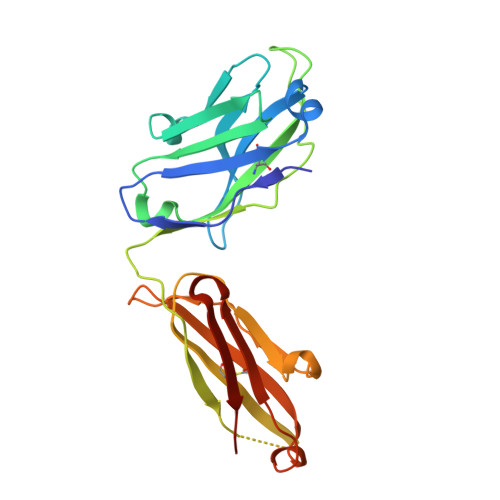
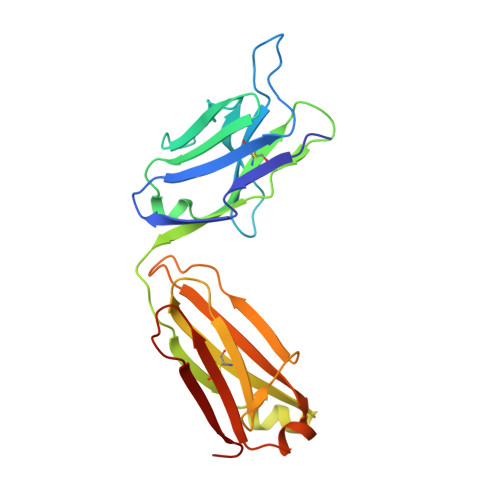
Structural basis for norovirus neutralization by an HBGA blocking human IgA antibody.
Shanker, S., Czako, R., Sapparapu, G., Alvarado, G., Viskovska, M., Sankaran, B., Atmar, R.L., Crowe, J.E., Estes, M.K., Prasad, B.V.(2016) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113: E5830-E5837
- PubMed: 27647885
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1609990113
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5KW9 - PubMed Abstract:
Human noroviruses (HuNoVs) cause sporadic and epidemic gastroenteritis worldwide. They are classified into two major genogroups (GI and GII), with each genogroup further divided into multiple genotypes. Susceptibility to these viruses is influenced by genetically determined histo-blood group antigen (HBGA) expression. HBGAs function as cell attachment factors by binding to a surface-exposed region in the protruding (P) domain of the capsid protein. Sequence variations in this region that result in differential HBGA binding patterns and antigenicity are suggested to form a basis for strain diversification. Recent studies show that serum antibodies that block HBGA binding correlate with protection against illness. Although genogroup-dependent variation in HBGA binding specificity is structurally well characterized, an understanding of how antibodies block HBGA binding and how genotypic variations affect such blockade is lacking. Our crystallographic studies of the GI.1 P domain in complex with the Fab fragment of a human IgA monoclonal antibody (IgA 5I2) with HBGA blocking activity show that the antibody recognizes a conformational epitope formed by two surface-exposed loop clusters in the P domain. The antibody engulfs the HBGA binding site but does not affect its structural integrity. An unusual feature of the antigen recognition by IgA 5I2 is the predominant involvement of the CDR light chain 1 in contrast to the commonly observed CDR heavy chain 3, providing a unique perspective into antibody diversity in antigen recognition. Identification of the antigenic site in the P domain shows how genotypic variations might allow escape from antibody neutralization and exemplifies the interplay between antigenicity and HBGA specificity in HuNoV evolution.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Verna and Marrs McLean Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030.